Understanding the Science Behind the Greenhouse Effect and Its Impact on Our Planet. Discover The greenhouse effect’s science & its impact on Earth. Learn how it warms our planet & why it matters To all of us. Let’s explore together!
What is Understanding The Science Behind The Greenhouse Effect & Its Impact on Our Planet & how does it work?
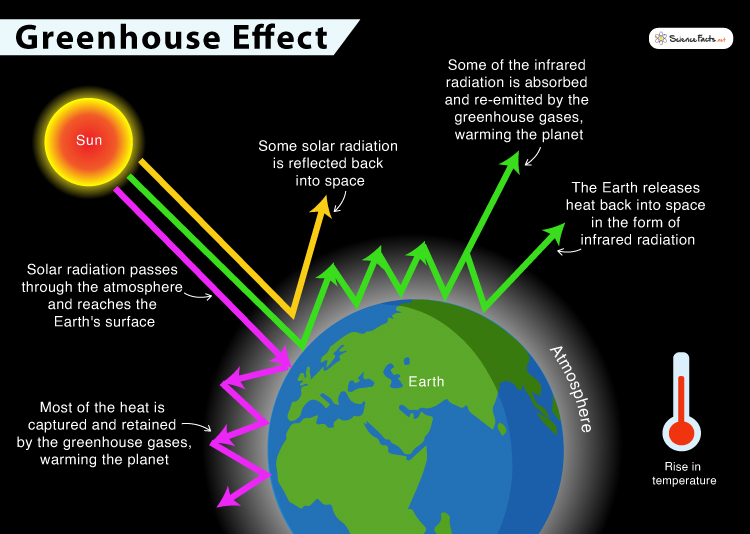
Greenhouse effect describes warming process within Earth’s atmosphere. Sunlight warms surfaces, releasing heat as infrared radiation. Certain gases trap this heat, preventing escape. Common greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, & nitrous oxide. As concentrations rise, atmosphere retains more heat. This process leads To global temperature increase, creating different climate patterns.
Brief history of Understanding The Science Behind The Greenhouse Effect & Its Impact on Our Planet
Scientific exploration began in 19th century. Scientists like John Tyndall identified gases responsible for warming. Later, figures such as Svante Arrhenius predicted future temperature changes. Measurements of carbon dioxide levels intensified during 20th century. Observations confirmed rising temperatures linked with increased greenhouse gas emissions. Awareness of climate change emerged as a significant issue globally.
How To implement Understanding The Science Behind The Greenhouse Effect & Its Impact on Our Planet effectively
Education serves as a foundation. Informing communities helps raise awareness about climate issues. Promoting renewable energy reduces reliance on fossil fuels. Enhancing energy efficiency minimizes waste across various sectors. Supporting sustainable practices encourages responsible consumption habits. Engaging with policymakers fosters effective environmental regulations.
Key benefits of using Understanding The Science Behind The Greenhouse Effect & Its Impact on Our Planet
Enhanced awareness can drive community action. Understanding promotes proactive measures against climate change. Using this knowledge encourages better resource management. Improved air quality results from reduced emissions. Sustainable practices protect biodiversity & ecosystems. Actions taken today benefit future generations.
Challenges with Understanding The Science Behind The Greenhouse Effect & Its Impact on Our Planet & potential solutions
Resistance from industries poses significant challenges. Economic interests often conflict with environmental priorities. Misinformation about climate change complicates public perception. Effective communication strategies need development for better clarity. Collaboration between scientists & communities fosters understanding. Policies should incentivize green technologies & practices.
Future of Understanding The Science Behind The Greenhouse Effect & Its Impact on Our Planet
Emerging technologies will transform energy production. Innovations in carbon capture could minimize emissions significantly. Greater emphasis on international cooperation becomes crucial. Public engagement will grow with increased awareness. Future generations will hold key responsibility for sustainable practices. Societies may shift towards circular economies, reducing waste sustainably.

Understanding Science Behind Greenhouse Effect & Its Impact on Our Planet
Defining Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect refers To a natural process, where certain gases trap heat in atmosphere. This phenomenon maintains Earth’s temperature, allowing life To flourish. Without it, our planet would be too cold for human existence. Greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide, methane, & nitrous oxide, play a crucial role in this process. For more detailed information on how this process works, visit this link.
Before modern times, this effect kept global climate in balance. However, recent human activities have increased greenhouse emissions. Deforestation, industrial processes, & burning fossil fuels contribute significantly. Understanding how these actions affect natural cycles is essential for addressing climate challenges.
Many people may not grasp how interconnected our actions are with atmospheric changes. Each choice, whether personal or global, influences climate outcomes. As I reflect on my own journey of awareness, I realize how crucial knowledge about greenhouse gases became. My experiences have motivated me toward sustainable living, seeking To minimize my own carbon footprint.
Types of Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases come in various types, each with unique properties. Carbon dioxide (CO2) remains one of most abundant. This gas primarily originates from burning fossil fuels, like coal, oil, & gas. It holds heat in atmosphere, contributing significantly To global warming.
Methane, another potent greenhouse gas, comes from agricultural practices & waste management. Livestock, like cows, produce methane through digestion. Additionally, landfills release methane as organic waste decomposes. Understanding these sources helps illustrate how everyday activities contribute significantly. For further reading on climate science, please refer To this resource.
Nitrous oxide, though less prevalent, boasts significant warming potential. Agricultural fertilizers release this gas, affecting climate dynamics. On The other hand, fluorinated gases, produced in industrial processes, present additional challenges. These compounds can persist in atmosphere for long periods, enhancing greenhouse effect even further.
Role of Sunlight & Earth’s Atmosphere
Sunlight plays a vital role in nurturing life. This energy reaches Earth, heating its surface. Some of this heat escapes back into space, while greenhouse gases capture a portion. This balance creates a suitable climate for various ecosystems.
When excessive greenhouse gases accumulate, heat retention increases. As a result, average global temperatures rise. This warming leads To various environmental consequences. Oceans absorb much of this additional heat, which affects marine ecosystems.
Atmosphere’s structure helps regulate temperatures across regions. Warm air rises while cool air descends. This process creates weather patterns, influencing precipitation & climate. Any disturbances in this balance can lead To extreme weather events.
Impacts of Greenhouse Effect on Weather Patterns
Greenhouse effect leads To observable changes in weather patterns. As temperatures rise, more moisture evaporates from oceans. This moisture can intensify storms, causing floods in some areas, while drought may impact others.
Increased warmth also alters jet streams. These high-altitude winds significantly affect weather. Changes in jet streams often result in prolonged periods of heat or cold in specific regions. The unpredictability of weather presents challenges for agriculture & water resources.
Moreover, changing weather patterns can alter entire ecosystems. Species dependent on specific climates may struggle To survive as habitats shift. Some may adapt, while others face extinction. Biodiversity plays an essential role, maintaining ecosystems in harmony.
Environmental Consequences of Global Warming
Global warming, resulting from enhanced greenhouse effect, leads To numerous environmental challenges. Melting ice caps contribute directly To rising sea levels. Coastal cities face increased risks of flooding as water encroaches on land.
Additionally, extreme heat events pose health risks. Vulnerable populations without adequate resources may suffer. Urban environments can amplify these effects, creating heat islands. Mitigating these risks requires proactive measures To protect communities.
Wildfires become more prevalent due To prolonged dry spells. With changing weather patterns, regions once rich in flora may turn into arid landscapes. Ecosystems face threats as wildlife relocates, seeking more hospitable environments.
Human Influence on Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Human activities substantially contribute To greenhouse gas emissions. Industrial processes, such as manufacturing & energy production, have increased significantly. These activities release tremendous amounts of carbon dioxide into atmosphere.
Transportation also plays a vital role in emissions. Vehicles powered by fossil fuels emit large quantities of greenhouse gases. Transitioning toward cleaner energy sources, such as electric vehicles, holds promise for reducing these impacts.
Deforestation exacerbates The situation. Trees absorb carbon dioxide, acting as carbon sinks. When forests are cleared for agriculture or urban development, carbon stored within trees releases back into atmosphere. Sustainable forestry practices, along with afforestation efforts, can help mitigate these effects.
Potential Solutions To Mitigate Greenhouse Effect
Individuals & communities can take steps toward mitigating greenhouse effects. Adopting renewable energy sources, such as solar & wind, reduces reliance on fossil fuels. Transitioning toward clean energy can significantly decrease emissions.
Energy efficiency also plays a crucial role. Simple actions, like using energy-efficient appliances & insulative materials in homes, can lower energy consumption. Engaging in sustainable practices, such as recycling & composting, contributes positively as well.
On a larger scale, policies aimed at reducing emissions are essential. Governments must create & enforce regulations encouraging businesses & consumers To adopt sustainable practices. Implementing carbon pricing can provide economic incentives for reducing emissions Science Behind the Greenhouse Effect.
Understanding Climate Change Feedback Loops
Feedback loops create additional challenges within climate systems. For example, as temperatures rise, permafrost thaws. This thawing releases stored methane, further enhancing greenhouse effect. Such cycles illustrate how interconnected systems reinforce challenges.
Similarly, melting ice reduces Earth’s reflectivity. Less ice means darker surfaces absorb more sunlight. This creates a cycle of warming & ice loss. Understanding these feedback loops helps grasp risks associated with global warming.
Addressing these feedback loops requires comprehensive approaches. Reducing emissions can slow down these cycles. Climate education & awareness foster engagement, inspiring collective action. Each individual action contributes toward breaking these damaging cycles.
Advocacy & Climate Action
Advocating for climate action remains crucial. Grassroots movements encourage individuals To engage in sustainable practices. Many organizations work tirelessly, raising awareness & inspiring changes at local, national, & global levels.
Participating in community initiatives can create significant impact. Local gardens, clean-up events, & educational programs foster connection among residents. Supporting policies designed To limit emissions can help shape a more sustainable future.
Engaging with legislators ensures climate issues remain a priority. Voting for representatives committed To environmental protection strengthens efforts toward sustainability. Only through collective action can significant change occur.
Future of Our Planet in Relation To Greenhouse Effect
The future of our planet hinges upon how society addresses greenhouse effect challenges. Without proactive measures, climate disruptions will likely worsen. By fostering awareness & inspiring collective action, individuals can help mitigate adverse impacts.
Scientific advancements hold potential for new solutions. Innovations in carbon capture technology could transform greenhouse gas management. Renewable energy technologies continue To evolve, offering exciting possibilities for a more sustainable world.
Ultimately, adopting sustainable practices on a personal level will contribute tremendously. Each positive action, no matter how small, enriches collective efforts. Engaging with others will inspire communities, leading toward a healthier planet for future generations.
Key Features of Understanding Greenhouse Effect
- 📈 In-depth analysis of greenhouse gas types
- 🌐 Exploration of human impacts on climate
- 🌍 Examination of environmental consequences
- 🌱 Sustainable solutions for individuals
- 🔄 Feedback loops in climate systems
- 📣 Advocacy & collective action significance
- 🔮 Future outlook on planet’s climate

Understanding Greenhouse Effect
Greenhouse effect plays a crucial role in regulating Earth’s climate. This phenomenon occurs when certain gases trap heat within atmosphere. Without this effect, our planet would be too cold for life. Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, & nitrous oxide. These gases allow sunlight in but prevent some heat from escaping back into space. Life on Earth relies heavily on this natural process.
Human activities significantly enhance greenhouse effect. Burning fossil fuels, deforestation, & industrial processes increase concentration of these gases. As a result, more heat gets trapped, leading To global warming. Our climate’s stability depends on a delicate balance. Disruption threatens ecosystems, weather patterns, & human life.
Mechanism of Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect starts with solar radiation. Sunlight passes through atmosphere, warming Earth’s surface. Different wavelengths of light interact with various surfaces. Land, water, & vegetation absorb sunlight & release energy as heat. Greenhouse gases in atmosphere capture this heat, preventing quick escape into space.
A notable aspect involves feedback loops. For example, warming oceans release more water vapor, which acts as a greenhouse gas. This increases temperature further. Additionally, melting polar ice reduces sunlight reflection, causing further heating. These feedback mechanisms amplify initial changes, creating a cycle of escalation.
Impact on Climate Change
Climate change results from increased greenhouse gas emissions. Average global temperatures rise, causing extreme weather changes. Droughts, floods, hurricanes, & wildfires have become more frequent. These alterations jeopardize food security & water resources. Ecosystems face risks as habitats change too rapidly for species adaptation.
Some regions encounter intensified heatwaves, while others experience harsh cold spells. This irregular weather patterns pose challenges for agriculture. Farmers struggle with unpredictable growing seasons. Shifts in precipitation patterns affect crop yields, threatening food supply chains worldwide.
Effects on Biodiversity
Greenhouse effect impacts biodiversity considerably. As climates shift, many species face extinction. Ecosystems, which depend on specific temperature & rainfall patterns, can collapse. Changes force many animals & plants To migrate. Those unable To adapt face dire consequences, as habitats transform. Ecosystems become less stable as species numbers dwindle.
Coral reefs represent a prime example. Rising ocean temperatures cause coral bleaching, resulting in loss of marine life. Terrestrial ecosystems also experience similar effects. Plants & animals struggle as their habitats change around them. Maintaining biodiversity relies on understanding & addressing climate change issues.
Linking Climate Literacy & Action
Educating communities about greenhouse effects proves vital for sustainable practices. Programs promoting awareness lead individuals To make informed choices. Understanding climate change fosters a culture of sustainability. Grassroots movements challenge harmful practices & advocate for policy changes.
For further insights, explore resources like NASA’s Climate Kids. Young learners benefit from accessible explanations & engaging visuals. Additionally, The UCAR’s website offers excellent educational materials. These platforms empower communities To understand climate science.
Global & Local Efforts
Governments & institutions globally strive for emissions reduction. Agreements like Paris Accord aim To unite nations in combating climate change. Local communities also take action through conservation projects. Urban areas introduce green spaces & renewable energy solutions. Such initiatives contribute positively toward mitigating greenhouse impacts Science Behind the Greenhouse Effect.
Technology plays a pivotal role in these efforts. Innovations in clean energy reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Solar panels & wind turbines redefine energy production. Such advancements contribute significantly toward achieving sustainability goals. Sustainable transport options also emerge, minimizing fossil fuel consumption.
Personal Experience & Action
Witnessing effects firsthand provides powerful motivation for change. I noticed a shift in local climate patterns over years. Seasonal weather changes impacted familiar landscapes. More frequent storms & erratic temperatures troubled residents. Engaging neighbors inspired community efforts toward green initiatives. These experiences encourage personal responsibility & collective action.
Adverse Effects on Human Health
Greenhouse emissions contribute directly To health problems. Increased air pollution from vehicles & industries results in respiratory issues. Vulnerable populations, including children & elderly, face heightened risks. Urban areas often experience heat islands, intensifying heat-related illnesses.
Vector-borne diseases also thrive in changing climates. Warmer temperatures lead mosquitoes & other vectors To expand their ranges. This increase places more people at risk for diseases, such as malaria & dengue. Public health systems must adapt To these emerging threats.
Responses To The Greenhouse Effect
Addressing greenhouse effect requires concerted global efforts. Governments, organizations, & individuals must collaborate. Reducing carbon footprints through lifestyle changes benefits planet. Choosing renewable energy, eating less meat, & minimizing waste make positive impacts. Supporting policies geared toward sustainability enhances collective efforts.
Technological innovation aids in tackling these challenges. Carbon capture technologies aim To reduce atmospheric CO2 levels. Investment in sustainable agriculture practices promotes biodiversity & yields. Education & community engagement foster informed citizens. Spreading awareness leads To further momentum in green initiatives.
Comparison Table of Impact Factors
| Impact Factor 🌍 | Positive Effects ✅ | Negative Effects ❌ |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Renewable Energy | Reduces emissions | Initial cost of implementation |
| Climate Education | Informed citizenry | Resistance from skeptics |
| Community Engagement | Stronger local networks | Requires sustained commitment |
| Technological Innovation | More efficient processes | Possible unforeseen consequences |
| Sustainable Practices | Enhanced biodiversity | Behavior change resistance |
The Role of Policy in Climate Action
Government policies significantly influence climate action outcomes. Effective regulations limit emissions & promote sustainable practices. Incentives for renewable energy development encourage investment in green technologies. Expanding clean transport options also positively impacts overall emissions.
International cooperation plays a pivotal role. Nations must collaborate in addressing common challenges. Sharing technologies & resources encourages collective progress. Commitments made in global agreements can drive local actions that address climate change effectively.
Sustainability in Daily Life
Individuals also contribute through daily choices. Using public transport, cycling, or walking reduces greenhouse emissions. Incorporating native plants in gardens supports local biodiversity. Eating a balanced diet with less meat still meets nutritional needs, while having environmental benefits. Choosing local produce lowers carbon footprints.
Supporting businesses focused on sustainability encourages ethical practices. Shopping locally strengthens community resilience. Engaging in advocacy, volunteering for local projects, & participating in climate marches further drive awareness. Each action contributes toward a greater understanding of climate issues.
What is The greenhouse effect?
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms The Earth’s surface. When The Sun’s energy reaches The Earth, some of it is reflected back To space & The rest is absorbed, warming The planet. The Earth then radiates this energy back toward space in The form of infrared radiation.
What gases are involved in The greenhouse effect?
Greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, & water vapor, play a crucial role in The greenhouse effect. These gases trap heat in The atmosphere, preventing it from escaping back into space & thus warming The Earth.
How do human activities affect The greenhouse effect?
Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, & industrial processes, increase The concentration of greenhouse gases in The atmosphere. This enhanced greenhouse effect leads To more heat being trapped, contributing To global warming & climate change.
What are The consequences of an enhanced greenhouse effect?
The enhanced greenhouse effect leads To higher global temperatures, resulting in changes in weather patterns, more frequent extreme weather events, & rising sea levels. These changes can have significant impacts on ecosystems, human health, & agriculture.
How does The greenhouse effect contribute To climate change?
The greenhouse effect is a key driver of climate change. As more greenhouse gases accumulate in The atmosphere, they intensify The natural greenhouse effect, leading To global warming & associated climatic shifts that can impact weather, biodiversity, & sea levels Science Behind the Greenhouse Effect.
Is The greenhouse effect The same as global warming?
While The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon, global warming refers To The recent increase in Earth’s average temperature due To human-induced emissions of greenhouse gases. The greenhouse effect is a contributing factor To global warming, but they are not synonymous.
Can The greenhouse effect be reduced?
Yes, The greenhouse effect can be mitigated by reducing greenhouse gas emissions through various means such as transitioning To renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, & protecting forests. International agreements, like The Paris Agreement, also aim To limit emissions globally.
What role do plants play in The greenhouse effect?
Plants play a vital role in The greenhouse effect by absorbing carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, which helps To reduce The concentration of greenhouse gases in The atmosphere. Forests & vegetation act as carbon sinks, storing carbon & regulating The climate.
What can individuals do To combat The greenhouse effect?
Individuals can take action by reducing energy consumption, using public transport, supporting renewable energy initiatives, recycling, & advocating for policies that address climate change. Small changes in daily habits can collectively make a significant impact.
How does The greenhouse effect impact weather patterns?
The greenhouse effect can disrupt weather patterns by altering temperature & precipitation distributions. This can lead To more intense storms, longer droughts, & changes in seasonal weather, affecting agriculture, water supply, & natural ecosystems.
Are there any natural factors that influence The greenhouse effect?
Yes, natural factors such as volcanic eruptions, solar radiation variations, & ocean currents can influence The greenhouse effect. These factors can either enhance or mitigate The effects of greenhouse gases on The Earth’s climate.
Conclusion
In simple terms, The greenhouse effect is like a warm blanket for our planet. It keeps The Earth cozy enough To support life. However, human activities are thickening that blanket, leading To more heat & changing climates. This can cause serious problems, like extreme weather & rising sea levels. By understanding this effect, we can make smarter choices, like reducing emissions & using cleaner energy. Every little action counts in protecting our environment. Together, we can work towards a healthier planet. It’s not just about science; it’s about our future & The world we’ll leave behind for generations To come.