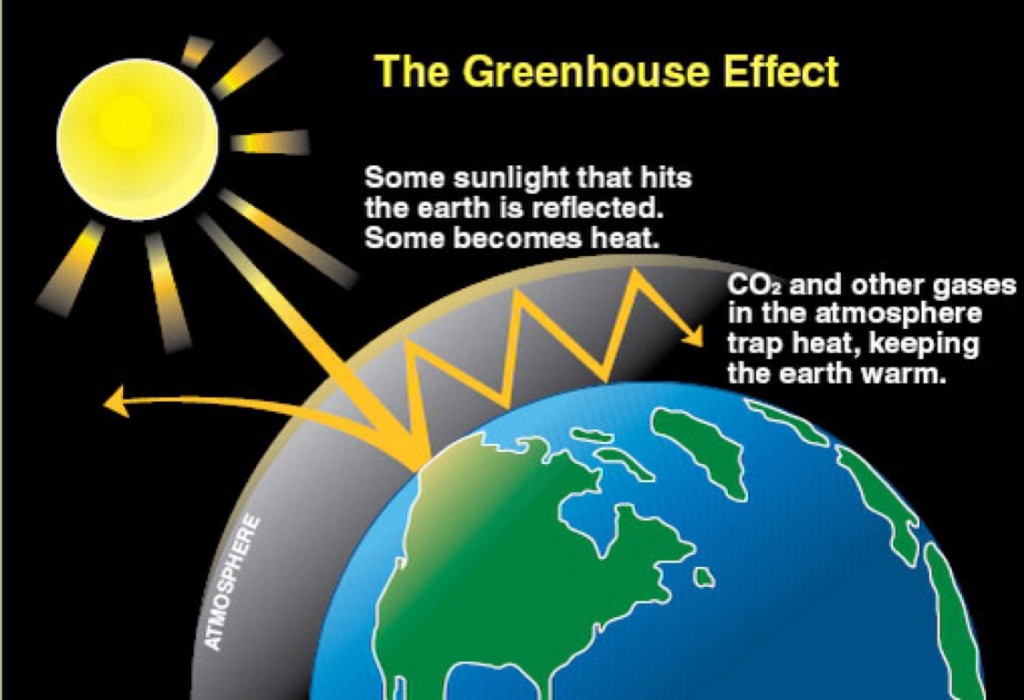
Understanding the Impact of Greenhouse Gases on Our Planet’s Climate. Discover how greenhouse gases affect our planet’s climate. Learn about their role in warming our Earth & why it’s crucial To take action for a healthier future.
What is Understanding The Impact of Greenhouse Gases on Our Planet’s Climate & how does it work?
Greenhouse gases trap heat in atmosphere. This process causes Earth’s temperature To rise. Carbon dioxide, methane, & nitrous oxide contribute significantly. Their increasing concentration leads To climate change. Human activities, like burning fossil fuels, enhance this effect. Understanding these gases helps grasp climate dynamics.
Brief history of Understanding The Impact of Greenhouse Gases on Our Planet’s Climate
Early research dates back over a century. Scientists began studying atmospheric effects in 19th century. John Tyndall discovered gases absorb infrared radiation. Later studies by Svante Arrhenius connected emissions & temperature rise. Awareness grew through 20th century. Major reports detailed these relationships, shaping modern policy.
How To implement Understanding The Impact of Greenhouse Gases on Our Planet’s Climate effectively
Education plays a crucial role. Schools should integrate environmental science. Public campaigns can raise awareness about climate issues. Policies should encourage sustainable practices. Reducing carbon footprints remains essential. Communities can promote renewable energy sources.
Key benefits of using Understanding The Impact of Greenhouse Gases on Our Planet’s Climate
Enhanced understanding fosters informed decision-making. Communities can adopt sustainable habits. Fear of climate change diminishes with knowledge. Businesses can operate more sustainably, reducing costs. Healthy ecosystems benefit from reduced emissions. Overall, a balanced approach enhances life quality.
Challenges with Understanding The Impact of Greenhouse Gases on Our Planet’s Climate & potential solutions
Resistance exists against change. Some deny climate science, hindering progress. Misinformation spreads rapidly online. Solutions include robust education efforts. Engaging communities helps combat confusion. Collaboration across sectors creates a unified response.
Future of Understanding The Impact of Greenhouse Gases on Our Planet’s Climate
Technological advances may revolutionize energy use. Innovations could decrease emissions significantly. Increased investment in renewable sources looks promising. Global cooperation will be vital for success. Future generations must prioritize sustainability practices. Together, societies can build a healthier planet.
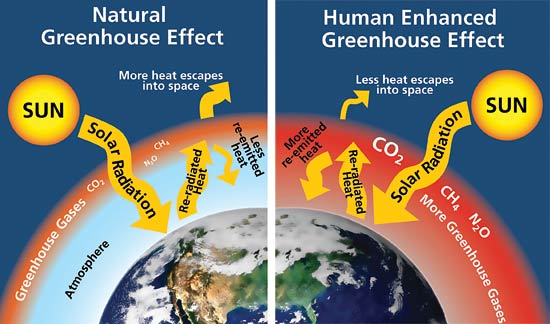
Understanding Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases play a crucial role in regulating Earth’s temperature. They trap heat in atmosphere, creating a phenomenon known as The greenhouse effect. This effect maintains a temperature necessary for life. However, human activities have significantly increased concentrations of these gases. Thus, climate changes are becoming more apparent worldwide.
Common greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, & nitrous oxide. Each gas contributes differently To warming. For detailed information on greenhouse gases contributing To global warming, visit this article.
Understanding sources of these gases is vital. Fossil fuel combustion, agriculture, & land use changes generate significant emissions. In my own experience, observing smoke rising from factories made me realize our choices directly impact environment. Each individual’s or organization’s decision counts. Awareness can lead To actions that mitigate these emissions.
Major Greenhouse Gases
Carbon dioxide (CO2) remains one of most prevalent greenhouse gases. Its production primarily stems from fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, & industrial processes. CO2 levels have reached record highs over past decades. This gas has a long lifespan in atmosphere, intensifying effects over time.
Methane (CH4) is another potent greenhouse gas. Though less abundant, methane traps heat more effectively than CO2. Agricultural practices, landfills, & natural gas production release methane into atmosphere. Addressing these sources holds immense potential for reducing global warming.
Nitrous oxide (N2O) contributes significantly, especially in agricultural settings. It’s released during fertilization processes & other activities. Unlike carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide emissions have a stronger heat-trapping capacity. Reducing agricultural reliance on chemical fertilizers can minimize nitrous oxide output.
Human Activities & Emissions
Human activities drive The rise in greenhouse gas concentrations. Industrialization led societies toward fossil fuel dependence. As a result, carbon emissions from power plants, vehicles, & heating systems continue escalating. This energy consumption pattern severely impacts climate stability.
Urbanization also influences greenhouse gas emissions. Growing cities often mean increased transportation & energy consumption. Urban heat islands form, raising localized temperatures. Creating sustainable transportation systems & energy-efficient buildings can help mitigate this issue.
Furthermore, agriculture plays a significant role in emissions. Intensive farming practices release greenhouse gases such as methane & nitrous oxide. Sustainable farming methods can lessen impact. For insights on greenhouse gases, check this link.
Effects on Climate
Greenhouse gases directly affect climate patterns. An increase in global temperatures leads To altered weather patterns. These changes contribute To severe weather events, droughts, & flooding. Ecosystems are becoming increasingly vulnerable due To rapid climate shifts.
Coral reefs suffer from temperature increases, leading To bleaching & death. Marine life faces massive ecosystem disruptions. Species extinction rates are accelerating as habitats change. Such changes demand immediate attention & action from governments & individuals alike.
Air quality also deteriorates due To these gases. Unhealthy pollution levels harm human health, causing respiratory issues & other complications. Addressing greenhouse gas emissions can simultaneously improve public health & climate health.
Mitigation Strategies
Mitigating greenhouse gas emissions requires collective efforts. Transitioning toward renewable energy sources greatly reduces dependency on fossil fuels. Solar, wind, & hydroelectric power offer viable alternatives. Promoting clean energy technologies can decrease emissions significantly.
Additionally, enhancing energy efficiency in buildings & industries also plays a role. Implementing smarter designs & retrofitting existing structures can lower energy consumption. Investing in efficient appliances further contributes towards emission reductions.
Lastly, reforestation & afforestation efforts can absorb carbon dioxide. Planting trees restores natural carbon sinks, mitigating climate change. Communities can engage in tree-planting initiatives strengthening local ecosystems.
Global Initiatives & Agreements
Nations worldwide work collaboratively To combat climate change. International agreements, such as The Paris Agreement, outline goals for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Participating countries aim To limit global temperature rise To below 2 degrees Celsius. Such commitments seek To ensure a sustainable future for generations.
Governments have also set individual national targets for emissions reductions. Various initiatives encourage businesses & individuals alike To lower their carbon footprints. Such policies include tax incentives for adopting renewable technologies or participating in carbon trading schemes.
Public awareness campaigns serve a vital role. Educating people about climate change fosters a collective response. Grassroots movements inspire individuals & communities To take action. Activism promotes The need for change at local & global levels.
Future Perspectives
The future concerning greenhouse gas emissions remains critical. Technological advancements can provide new solutions, aiming for a low-carbon economy. Innovations in energy storage & carbon capture hold promise for reducing atmospheric gas concentrations.
Research into sustainable agriculture practices continues evolving. Techniques such as agroforestry & permaculture may enhance food production while preserving ecosystems. More sustainable food systems can decrease agricultural-related emissions.
Moreover, adjusting consumption habits proves essential. Promoting sustainable lifestyles can significantly lower individual carbon footprints. Awareness around purchasing choices, energy usage, & transportation emphasize individual responsibility toward climate change.
Space for Improvement
Even with significant advancements, challenges persist. Global disparities in emissions remain a concern. Developing nations often bear The brunt of climate change effects while contributing comparatively less To emissions. Supporting these nations through financial aid & technology transfer can enhance their resilience.
Public policy plays a fundamental role in shaping future pathways. Policymakers need encouragement To adopt measures that reflect sustainability goals. Fostering collaboration among industries, governments, & communities can enhance climate policy efficiency.
Lastly, continuous research & monitoring are essential. Understanding how greenhouse gas concentrations affect climate patterns over time can guide decision-making. Collective action towards transparency can generate trust, spurring more robust climate actions.
- ✨ Emphasis on Renewable Energy Sources
- 🌱 Sustainable Agriculture Practices
- 💡 Promotion of Energy Efficiency
- 🌍 International Cooperation & Agreements
- 🌳 Reforestation & Conservation Efforts
- 🔍 Ongoing Research & Innovations
- 🏙️ Urban Planning for Sustainable Cities

Understanding Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gases trap heat within atmosphere. These gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), & nitrous oxide (N2O). Emissions arise from numerous human activities, such as burning fossil fuels & agriculture. Human activities have increased concentrations of these gases dramatically over past century. This increase leads directly To global warming & climate change.
Carbon dioxide has become most significant greenhouse gas. This gas stems primarily from combustion of fossil fuels. Such activities occur in industries, power plants, & vehicles. Additionally, deforestation contributes significantly. Trees absorb CO2, thus losing forests exacerbates CO2 levels.
Methane, while less abundant, possesses 25 times greater heat-trapping capacity. Major sources of methane include livestock digestion, rice paddies, & landfills. Methane emissions often occur during extraction of natural gas & oil. Efforts aimed at curbing methane emissions yield notable climate benefits.
Global Warming & Climate Change
Global warming refers To long-term rise in Earth’s average temperature. Climate change encapsulates broader shifts, including extreme weather patterns & changing ecosystems. Greenhouse gases play crucial role in these phenomena. Their presence intensifies greenhouse effect, causing heat retention within atmosphere.
Many regions experience rising temperatures & altered precipitation patterns. Some areas suffer from more intense droughts, while others face severe flooding. Consequently, such climatic shifts lead To food & water scarcity. These variables increase competition over limited resources.
Additional issues arise from melting polar ice caps. With glacial reductions, sea levels rise, threatening coastal communities. Scientists attribute this rise directly To climate change. Such effects underscore urgency toward addressing greenhouse gas emissions. For comprehensive information on sources of greenhouse gas emissions, refer To this EPA link.
Impact on Ecosystems
Greenhouse gases lead To shifting habitats for wildlife. Many species face challenges adapting To new conditions. Altered temperatures affect breeding & migration patterns significantly. This disruption threatens biodiversity across ecosystems.
Coral reefs exemplify vulnerable ecosystems. Increased water temperatures lead To coral bleaching. Bleached corals lose color & essential nutrients. Such stressors threaten entire marine ecosystems dependent on healthy coral habitats.
Furthermore, changes in precipitation impact plant growth. Some regions see increased growth due To warmer temperatures. Others may struggle due To prolonged droughts. Such variations disrupt food chains & alter ecosystem dynamics.
Climate Change Effects on Agriculture
Agriculture feels profound effects from climate change. changing temperatures & precipitation patterns disrupt traditional farming practices. Shifts may lead To crop failures, affecting food supply chains. Farmers increasingly face challenges in producing resilient crops.
Excessive heat can hinder crop yield. Fertility declines & pests thrive under warmer conditions. Such situations necessitate adaptations in farming methods. Farmers frequently invest in research toward climate-resilient crops.
Moreover, changing water availability complicates irrigation. Water scarcity forces farmers toward more effective practices. Sustainable farming techniques gain momentum as farmers respond To evolving challenges.
Strategies for Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Addressing greenhouse gas emissions requires collective action. Multiple strategies exist, specializing in various sectors. Transitioning toward renewable energy sources becomes a priority. Solar & wind energy produce zero emissions, helping mitigate climate change.
Enhancing energy efficiency plays significant role. Improved technologies in buildings reduce energy consumption effectively. Investing in energy-efficient appliances & practices leads many households toward lower emissions.
Transportation represents another crucial area. Encouraging public transport & electric vehicles minimizes fossil fuel reliance. Infrastructure improvements promote sustainable commuting options, thereby reducing congestion & emissions.
Government Policies & Climate Agreements
Governments hold key responsibility for regulating greenhouse gas emissions. Policy frameworks like The Paris Agreement aim To limit global temperature rise. Nations commit To reducing emissions, fostering international collaboration.
Carbon pricing emerges as an effective policy tool. This approach encourages businesses & individuals To reduce their carbon footprints. By placing a price on carbon, emissions become less attractive.
National regulations also foster climate action. Enhanced emissions standards for vehicles lead manufacturers toward cleaner technologies. Such policies create a more sustainable future for subsequent generations.
Community Awareness & Education
Grassroots movements play critical role in combatting climate change. Initiatives aimed at raising awareness promote public understanding. Education empowers individuals To adopt sustainable practices.
Encouraging community gardens fosters local food production. These initiatives reduce transportation emissions while promoting biodiversity. Moreover, sharing knowledge within communities strengthens resilience against climate change.
Engaging youth in environmental advocacy builds future leaders. Educating schools on climate impacts fosters awareness from early ages. As individuals become informed, collective action gains momentum.
Personal Reflections on Climate Advocacy
My journey toward climate advocacy began unexpectedly. Attending a community workshop opened my eyes. I discovered impactful solutions available for individuals & communities. Since then, I have been actively involved in several initiatives. Planting trees & promoting renewable energy continue energizing my efforts.
Comparative Analysis of Greenhouse Gases
| Gas Type 🌍 | Heat-Trapping Potential 💨 | Sources 🌱 | Global Warming Potential Over 100 Years 📈 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Dioxide | Moderate | Fossil fuels, deforestation | 1 |
| Methane | High | Agriculture, landfills | 25 |
| Nitrous Oxide | High | Agriculture, fossil fuels | 298 |
The Role of Technology in Mitigating Emissions
Advancements in technology offer promising solutions. Clean energy innovations transform energy sectors swiftly. Wind, solar, & hydroelectric systems contribute significantly. These sources produce sustainable energy while minimizing emissions.
Energy storage technology further enhances renewables. Improved batteries allow energy capture during peak production. Such systems ensure reliable power availability, especially during demand surges. This innovation addresses one major challenge in renewable energy deployment Understanding the Impact of Greenhouse Gases.
Carbon capture technology also gains traction. This technology captures CO2 before entering atmosphere. Captured carbon can undergo utilization or sequestration. Continued development will pave pathways toward effective emissions reduction.
International Perspectives on Climate Action
Various countries approach climate action uniquely. Some regions invest heavily in renewable energy. Others emphasize adaptation strategies, prioritizing resilience. These differences highlight challenges faced on a global scale.
Developing nations, often more vulnerable, differ in capacity. Financial constraints impact their ability To mitigate emissions. International collaborations foster knowledge sharing & resource allocation.
Global initiatives encourage comprehensive approaches. Agreements like COP aim for collective action. Nations commit To reducing greenhouse gases while adapting strategies tailored for individual circumstances.
For more information on this topic, visit Garden Beta. Their resources extensively cover climate action & sustainability practices.
What are greenhouse gases?
Greenhouse gases are gases in Earth’s atmosphere that trap heat. They let sunlight in but prevent some of The heat that The sunlight brings from leaving The atmosphere. The main greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, & water vapor.
How do greenhouse gases affect The Earth’s temperature?
They contribute To The greenhouse effect, which is a natural process that warms The Earth’s surface. When The Earth’s surface absorbs sunlight, it radiates energy in The form of infrared radiation. Greenhouse gases absorb this radiation & re-radiate it back To The surface, leading To an increase in temperature.
What are The main sources of greenhouse gas emissions?
The primary sources include fossil fuel combustion for energy, deforestation, industrial activities, agricultural practices, & waste management. Each of these activities releases different amounts & types of greenhouse gases into The atmosphere.
What is The impact of increased greenhouse gas concentrations?
Increased concentrations lead To global warming & climate change, resulting in more extreme weather events, rising sea levels, & disruptions To ecosystems. This can significantly affect biodiversity, agriculture, & human health.
Can greenhouse gas emissions be reduced?
Yes, emissions can be reduced through various strategies such as improving energy efficiency, transitioning To renewable energy sources, increasing carbon capture & storage technologies, & changing land-use practices. These measures can help limit The long-term impact of climate change.
What role do plants play in reducing greenhouse gases?
Plants absorb carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, which helps mitigate greenhouse gas concentrations in The atmosphere. Forests & other vegetation are vital carbon sinks & play a significant role in regulating The Earth’s climate.
How does deforestation contribute To greenhouse gas emissions?
Deforestation removes trees that absorb carbon dioxide, & The burning or decomposition of these trees releases stored carbon back into The atmosphere. This increases The concentration of greenhouse gases, consequently accelerating climate change.
What are The potential effects of climate change due To greenhouse gases?
Potential effects include more frequent & severe weather events, habitat loss, food & water shortages, & public health risks. These changes can have profound implications for human populations & natural ecosystems.
Are all greenhouse gases harmful?
Not all greenhouse gases are equally harmful. While some, like carbon dioxide, are necessary for life on Earth, excess concentrations can lead To harmful warming effects. Others, like methane, are much more potent in trapping heat, even in smaller amounts.
What actions can individuals take To reduce their greenhouse gas footprint?
Individuals can reduce their footprint by using energy-efficient appliances, reducing energy consumption, eating less meat & dairy, using public transport, recycling, & supporting policies aimed at reducing emissions.
What is The significance of international agreements on greenhouse gases?
International agreements, like The Paris Agreement, aim To unite nations in efforts To reduce greenhouse gas emissions globally. These agreements provide frameworks for reducing emissions & adapting To climate change, promoting cooperation & sustainability.
Conclusion
In summary, greenhouse gases play a crucial role in shaping our planet’s climate. They help keep our Earth warm, but too much of them can lead To serious problems, like extreme weather & rising sea levels. By understanding how these gases work, we can make smarter choices To reduce their emission. Simple actions, like using less energy & choosing cleaner transportation, can make a big difference. Together, we can take steps To protect our environment & create a healthier planet for future generations. Every small change counts, so let’s stay informed & do our part!