Understanding Methane: Its Role as a Greenhouse Gas and Environmental Impact. Discover The basics of methane, its role as a greenhouse gas, & how it affects our environment. Learn why understanding it is crucial for our planet’s future!
What is Understanding Methane: Its Role as a Greenhouse Gas & Environmental Impact & how does it work?
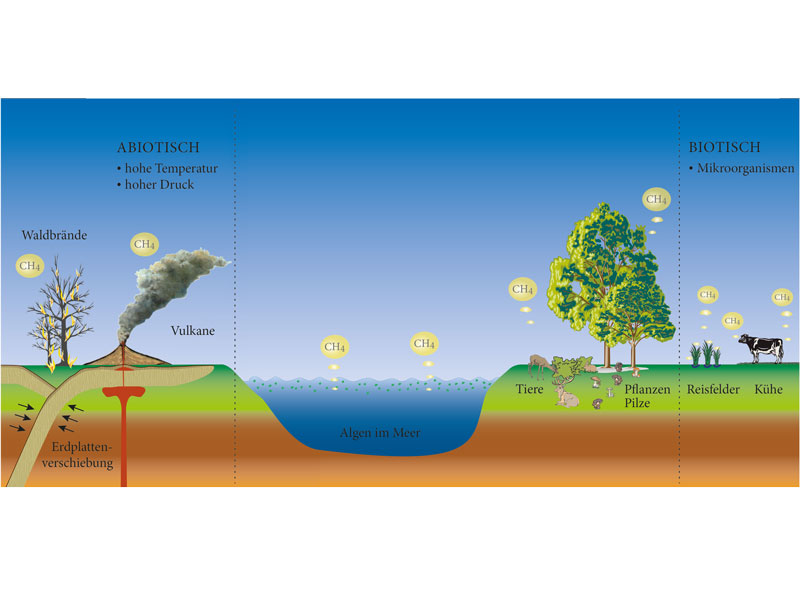
Methane serves as a potent greenhouse gas. Its warming potential exceeds carbon dioxide. This compound traps heat in Earth’s atmosphere. Understanding methane’s qualities reveals its significant impact. Sources include agriculture, landfills, & natural gas production. Microbial activity in anaerobic environments generates methane gas.
Brief history of Understanding Methane: Its Role as a Greenhouse Gas & Environmental Impact
Researchers first identified methane in 1776. Awareness regarding its greenhouse effect began in The 1990s. Studies showed methane contributes more heat than carbon dioxide. Global efforts emerged To monitor & mitigate emissions. Protocols like The Kyoto Agreement highlighted methane reduction. Increasing knowledge has fueled campaigns globally.
How To implement Understanding Methane: Its Role as a Greenhouse Gas & Environmental Impact effectively
Effective strategies focus on emission reduction. Monitoring technologies help track methane levels accurately. Implementing best practices in agriculture cuts emissions significantly. Management of landfills with capture systems reduces gas release. Developing energy-efficient solutions minimizes reliance on fossil fuels.
Key benefits of using Understanding Methane: Its Role as a Greenhouse Gas & Environmental Impact
Reducing methane impacts climate positively. Improved air quality results from lower emissions. Effective management enhances energy efficiency in industries. Initiatives create economic opportunities, especially in renewable sectors. Increased awareness can inspire community engagement on environmental issues.
Challenges with Understanding Methane: Its Role as a Greenhouse Gas & Environmental Impact & potential solutions
Many obstacles hinder effective methane management. Political will varies across regions. Public awareness remains low in some communities. Solutions include education campaigns promoting best practices. Technologies for capturing methane must improve as well. Incentivizing reduction initiatives encourages participation.
Future of Understanding Methane: Its Role as a Greenhouse Gas & Environmental Impact
Future trends show potential for greater innovation. Advancements in technology will enhance monitoring capabilities. Science might yield new methods for reducing emissions effectively. Continued collaboration among nations could strengthen global responses. Public consciousness around environmental issues will likely increase.

Understanding Methane: Its Role as a Greenhouse Gas & Environmental Impact
Origins of Methane Emissions
Methane, often produced through both natural processes & human activities, plays a crucial role as a greenhouse gas. Sources of methane emissions include agriculture, landfills, & fossil fuel extraction. In agriculture, livestock digestion & manure contribute significantly. Landfills produce methane as organic waste decomposes anaerobically, without oxygen. Additionally, oil & natural gas production release methane during extraction & transport. Understanding these diverse sources helps identify potential interventions.
Furthermore, methane has a much stronger heating effect than carbon dioxide. While carbon dioxide remains in atmosphere for centuries, methane persists for about a decade. Thus, even short-term increases in methane levels badly impact climate change. For more information on methane emissions & their impact, visit this article.
Individual actions can greatly influence methane emissions. Simple lifestyle adjustments, such as reducing meat consumption or minimizing food waste, help tackle this pressing issue. Communities should unite in reducing methane footprints while remaining cognizant of various emission sources. Together, proactive approaches can lead toward a healthier planet.
Methane’s Strength as a Greenhouse Gas
Methane possesses significant heat-trapping abilities. Its global warming potential stands at approximately 25 times greater than that of carbon dioxide over a 100-year period. This means methane has a profound influence on Earth’s climate. Even short atmospheric presence amplifies warming through various mechanisms, including The greenhouse effect.
Understanding these dynamics underscores methane’s importance within larger climate change discourse. Addressing methane emissions becomes paramount, not only for mitigating climate change but for improving air quality, as methane contributes To ozone formation at ground level. Through concerted actions, society can tackle this intricate challenge effectively.
In my experience, learning about methane’s effects reshaped how I view sustainability. I began exploring where my food originates. Decisions about diet drastically influence overall methane production in agriculture. By becoming more mindful about consumption, one can directly contribute toward minimizing methane emissions. This journey has truly inspired me.
How Methane Affects Climate Change
Methane’s contribution toward climate change escalates due To its capacity for heat absorption. As emissions increase & concentrations rise, global temperatures follow suit. Such changes lead To severe weather patterns, including more frequent & intense storms, droughts, & heatwaves. Ecosystems struggle To adapt, while species face extinction.
Moreover, accumulating scientific research links methane levels with detrimental effects on human health. Air pollution exacerbated by methane emissions leads To respiratory issues & other health complications. Therefore, addressing methane becomes imperative not only for ecological stability but also for public health preservation.
Innovation & technology promise potential solutions. Enhancements in agriculture, waste management techniques, & energy production can significantly reduce methane emissions. Leveraging renewable energy sources & improving resource efficiency present vital opportunities that society cannot ignore. Solutions lie in embracing environmentally friendly practices & sustainable innovations.
Challenges in Methane Reduction
Economic Factors Involved
Addressing methane emissions poses several economic challenges. Various industries, including agriculture & fossil fuels, often resist drastic changes due To profitability concerns. Transitioning from conventional practices toward more sustainable models can require significant investments. Many businesses fear potential losses associated with adopting new technologies.
Government regulations & policies can create incentives for companies. Implementing carbon pricing could encourage businesses toward lower emissions. Additionally, subsidies for renewable energy technologies can support transitions, fostering long-term sustainability. Companies embracing environmentally responsible practices often unlock benefits, ranging from enhanced reputation To increased market share.
Public support plays an essential role in overcoming resistance. Education & awareness about climate impacts can galvanize community backing for sustainable practices. When consumers prioritize environmentally friendly options, businesses feel pressured To follow suit. A united front of informed citizens can drive momentum toward reducing methane emissions effectively.
Technological Innovations
Cutting-edge technological innovations offer pathways for methane reductions. New methods for capturing methane during wastewater treatment, landfills, & agricultural processes provide real solutions. For instance, anaerobic digestion processes convert waste into renewable energy. These technologies not only curtail emissions but also generate electricity & biofuels.
Monitoring technologies also evolve, helping track methane emissions accurately. Satellite imaging & aerial surveillance can identify leaks during natural gas extraction. Businesses can adopt preventive measures To mitigate emissions proactively, thus fostering accountability within industries. Utilizing these innovations enables strategic planning & efficient resource allocation.
Additionally, research into alternative agricultural practices fosters sustainable farming. Crop rotations, cover cropping, & other methods can enhance soil health while reducing methane emissions. Modern practices help strike a balance between food production & environmental preservation, essential for global stability. Adopting these advancements can empower farmers & reshape agricultural paradigms.
Policy Initiatives & International Cooperation
Effective policy initiatives are necessary for meaningful methane reduction. Governments must prioritize regulations aimed at curbing emissions across various sectors. Policymakers can spearhead strategies designed To minimize landfill waste & incentivize sustainable agricultural practices. International cooperation is equally vital, as climate change transcends borders.
Agreements such as The Paris Accord emphasize global commitments toward reducing greenhouse gas emissions, including methane. Participating nations should collaborate on strategies tailored To local contexts. Sharing best practices while securing funds for developing countries can foster significant progress in combating methane emissions worldwide.
Grassroots movements often drive local initiatives, providing effective models for policy change. Communities that hold businesses accountable often lead successful campaigns focused on climate action. Engaging citizens in policy discussions reinforces democratic principles while empowering local solutions. This synergy between community advocacy & policy initiatives can uncover innovative routes toward sustainable living.
Impacts on Biodiversity & Ecosystems
Effects on Marine Life
Methane emissions have profound effects on marine ecosystems. Increased warming results in ocean acidification, jeopardizing marine biodiversity. Coral reefs suffer, leading To habitat loss for countless aquatic species. This unravels entire food webs & threatens livelihoods dependent on healthy ecosystems.
Moreover, changes in ocean temperatures impact migratory patterns of various fish species. Communities that rely on fishing often bear economic burdens due To declining fish populations. Studying these intricate relationships allows researchers To understand better how methane emissions exacerbate challenges faced by marine life. Conservation efforts must consider these variables as marine ecosystems evolve rapidly.
Collaboration between scientists, communities, & policymakers can develop strategies focused on ecosystem resilience. Protecting & restoring coastal habitats can serve as a buffer against temperature fluctuations. Innovative approaches can foster sustainable fisheries while nurturing vital marine habitats. Raising awareness about these interconnected systems remains critical for successful conservation efforts.
Impacts on Terrestrial Ecosystems
Lands affected by methane emissions witness changes in plant diversity & soil health. As climate change accelerates, essential habitats face degradation. These shifts lead toward loss of biodiversity, impacting not only flora but also fauna reliant on various ecosystems. Healthy landscapes support diverse species & mitigate flooding & erosion.
Heightened temperatures also alter precipitation patterns, affecting vegetation growth. Regions once abundant with plant life may transition toward arid landscapes, straining local wildlife populations. Understanding these dynamics helps guide conservation efforts aimed at protecting vulnerable species & their habitats.
Resource management plays a vital role in sustaining terrestrial ecosystems. Sustainable land practices, such as agroforestry, can foster healthier environments while capturing carbon in soils. Implementing restoration projects can rejuvenate degraded areas, ensuring diverse ecosystems thrive for generations. These concerted efforts create resilience among ecosystems, benefiting both wildlife & humanity.
Human Health Concerns
Methane’s influence extends beyond environmental impacts, as human health suffers several adverse effects. Increased air pollution, predominantly caused by methane emissions, leads To respiratory issues & other health problems. Ground-level ozone forms when methane reacts with other pollutants, exacerbating asthma & other conditions.
Vulnerable populations, particularly children & The elderly, face heightened risks from poor air quality. Urban areas with high methane emissions experience higher rates of hospitalization due To respiratory-related illnesses. Understanding these links allows communities & policymakers To prioritize health & safety measures while addressing climate change.
Empowering citizens with knowledge about these health risks promotes active engagement in climate action. Education on air quality & its impact on health can motivate individuals toward sustainable lifestyle choices. Advocating for clean air initiatives can further enhance public health while championing a healthier planet.
- 🥦 Reduction of methane through dietary shifts
- 🔥 Technological advancements capturing methane
- 🌱 Sustainable agricultural practices
- ♻️ Waste management innovations
- 🌐 International cooperation for climate action
- 🌊 Protecting marine ecosystems
- 🏞️ Restoration of terrestrial habitats
Future Directions in Methane Management
Research & Development Needs
Future efforts must emphasize innovative research & development focused on methane management. Enhanced understanding of methane’s role across various sectors fosters strategic responses geared toward emissions reductions. Collaboration between scientists, industry experts, & communities can drive breakthroughs that yield solutions.
Investments in research provide opportunities for discovering new technologies aimed at methane capture & reduction. Innovation helps bridge gaps while addressing economic concerns related To sustainability. Developing networks between academia, industry, & governmental agencies can enhance synergies for tackling methane emissions collectively.
Furthermore, expanding education on methane’s implications is critical for societal engagement. Training programs & public outreach efforts cultivate awareness about methane emissions impacts. Increased understanding encourages informed decision-making regarding consumption & promotes active community engagement toward reducing emissions.
Role of Policy & Regulation
Effective policy & regulation play essential roles in shaping methane management strategies. Policymakers must prioritize legislative frameworks that incentivize low-emission technologies & practices. Variables such as carbon pricing can motivate companies toward innovative approaches that significantly reduce methane emissions.
Continued governmental engagement strengthens existing efforts while fostering accountability within industries. Collaborative frameworks connecting various stakeholders can bolster effectiveness. Transparent policies rewarding progress can create a culture geared toward sustainability, encouraging entities To adopt environmentally responsible practices.
Public involvement in policy discussions remains crucial for transparent decision-making. Grassroots movements that advocate for robust policies can inspire broader societal action while ensuring accountability. Every individual has a role in promoting policies conducive To reducing methane emissions & preserving a healthy planet.
Community Engagement & Action
Communities represent a vital component in tackling methane emissions at local levels. Grassroots initiatives empower residents To partake in sustainable practices, from reducing waste To prioritizing renewable energy options. Local advocacy shapes public discourse surrounding sustainability while cultivating collective awareness about methane emissions impacts.
Community-led educational programs can initiate discussions aimed at empowering individuals with knowledge. Schools & organizations can collaborate on projects addressing methane emissions within local contexts. Having forums for sharing experiences & best practices fosters a culture of sustainability & collective problem-solving.
Ultimately, a united community effort can catalyze meaningful change. Collaborative strategies that engage citizens can lead toward practical solutions in addressing methane emissions. By working together, communities can create sustainable environments while safeguarding their health & well-being.
Conclusion & Further Steps
Understanding methane’s role as a greenhouse gas exposes its far-reaching environmental impacts. Addressing this urgent challenge requires multifaceted approaches encompassing various sectors, communities, & innovations. Continued commitment toward reduction efforts presents critical opportunities for creating a healthier environment for future generations.

Understanding Methane as a Greenhouse Gas
Methane (CH4) serves as significant greenhouse gas. Carbon dioxide remains well-known, but methane’s warming potential surpasses it. During a 20-year period, methane traps over 80 times more heat than carbon dioxide. This potency makes methane vital in discussions about climate change. Such properties place methane at forefront of environmental issues.
Sources of Methane Emissions
Many sources contribute To methane emissions. Agriculture stands out among these contributors. Livestock, especially cows, produce methane during digestion through a process called enteric fermentation. Manure management also results in methane release, as waste decomposes anaerobically.
Landfills also add significant methane emissions. Organic waste decomposes without oxygen in landfills, creating methane gas. This gas escapes into atmosphere unless captured & utilized. Additionally, fossil fuel production provides another source. Natural gas extraction, coal mining, & oil production release methane during activities.
Human activities exacerbate methane emissions. Urban development leads To increased food production & waste generation. Unsustainable farming practices further contribute methane release, impacting surrounding ecosystems. Managing emissions through innovative solutions remains crucial for reducing environmental impact.
Environmental Impact of Methane
Methane affects global warming & climate change. Its increased presence in atmosphere accelerates warming, impacting weather patterns & natural ecosystems. More extreme weather events, including droughts & floods, become common due To climate change driven by greenhouse gases like methane.
This gas doesn’t merely affect temperatures; ecosystems suffer, too. Fragile habitats, such as wetlands, face threats from warming. Biodiversity losses occur, leading To ecological imbalances. Many species struggle for survival under changing conditions, threatening global biodiversity.
Moreover, air quality suffers due To methane emissions. This gas can transform into ground-level ozone, a harmful air pollutant. This transformation leads To respiratory problems & other health issues in humans. Keeping communities healthy requires strong action against methane emissions.
Potential Solutions for Methane Reduction
Numerous strategies exist for reducing methane emissions. Improving livestock management offers one practical approach. Enhancing diets for cattle can minimize methane production during digestion. Farmers can also adopt practices such as rotational grazing, improving pasture health.
Waste management improvements play another key role. Landfills can capture methane gas for energy production instead of allowing it To escape. By utilizing technologies like anaerobic digestion, waste creates valuable resources instead of pollutants. This shift promotes sustainability & reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
Fossil fuel extraction methods require scrutiny. Implementing measures To reduce methane leaks during extraction remains crucial. Regular monitoring of infrastructure can help identify leaks quickly. Addressing these emissions not only benefits climate but also increases energy efficiency Role as a Greenhouse Gas.
Comparing Methane with Other Greenhouse Gases
| Greenhouse Gas 🌍 | Global Warming Potential (GWP) 🌡️ | Source 🚜 |
|---|---|---|
| Methane | 80 (20 years) | Agriculture, landfills, fossil fuels |
| Carbon Dioxide | 1 | Fossil fuel combustion, deforestation |
| Nitrous Oxide | 298 | Agricultural practices, waste management |
| Hydrofluorocarbons | 12,000 | Refrigerants, solvents |
| Aerosols | Variable | Industrial processes, transportation |
Impact on Human Health & Economy
Health impacts arise from methane emissions. As methane transforms into ozone, pollution levels rise. Such air quality deterioration leads To health issues for residents. Increased respiratory ailments create a burden on healthcare systems. This additional strain on resources requires urgent solutions.
Economically, methane emissions can have cascading effects. Communities suffering from pollution face higher healthcare costs. Businesses also bear increased operational expenses due To environmental regulations. This economic strain underlines The need for efficient methane management.
Investing in clean technology offers solutions. Companies can explore opportunities through innovative approaches. Efficient waste management systems not only reduce methane emissions but also support local economies. Building sustainable practices creates a win-win scenario for all parties involved.
Personal Experience with Methane Awareness
During my journey towards environmental awareness, I discovered methane’s impact. Engaging in various sustainability initiatives opened my eyes. I worked with organizations focused on reducing greenhouse gas emissions. My firsthand experience fueled a passion for addressing climate-related challenges.
Further Resources & Information
For deeper insights into methane reduction, access these resources. The Environmental Defense Fund provides significant information on methane’s role in climate change. Their article discusses critical opportunities for fighting climate change. Valuable information can be found at EDF climate initiatives.
Another beneficial resource can be found at The EPA. This site outlines essential information about greenhouse gases like methane & their implications. Explore more on greenhouse gases through this EPA overview.
Moreover, communities can find local solutions at GardenBeta. Participating in programs can create meaningful change at local levels.
Is methane considered a greenhouse gas?
Yes, methane is considered a greenhouse gas. It is much more effective than carbon dioxide at trapping heat in The atmosphere, making it a significant contributor To climate change.
How does methane compare To carbon dioxide in terms of greenhouse effect?
Methane has a much higher global warming potential than carbon dioxide over a short term, approximately 25 times more effective at trapping heat over a 100-year period.
What are The sources of methane emissions?
Methane emissions primarily come from natural sources like wetlands, & human activities such as agriculture, fossil fuel extraction, & waste management.
How long does methane stay in The atmosphere?
Methane has a relatively short atmospheric lifetime of about 12 years, but its heat-trapping ability means it can have a significant impact during that time.
What role does agriculture play in methane production?
Agriculture is a major source of methane, particularly through enteric fermentation in livestock & rice paddies, as well as from manure management.
Can methane be reduced or captured?
Yes, methane emissions can be reduced through better agricultural practices, waste management, & capturing it through technologies like anaerobic digestion.
What impact does reducing methane have on climate change?
Reducing methane emissions can have a rapid & significant impact on mitigating climate change, as it can lower The pace of warming in The short term.
Is methane responsible for any environmental issues other than greenhouse gas effects?
Yes, methane can contribute To air quality issues, leading To The formation of ground-level ozone, which is a harmful air pollutant & can affect human health.
How do methane emissions affect The atmosphere?
Methane emissions increase The concentration of greenhouse gases in The atmosphere, leading To enhanced greenhouse effect & contributing To global warming.
Are there any regulations regarding methane emissions?
Many countries have implemented regulations To monitor & reduce methane emissions, especially from significant sources like oil & gas, agriculture, & waste management.
Conclusion
Understanding methane is crucial for battling climate change. This potent greenhouse gas, often underestimated, plays a big role in warming our planet. It comes from various sources, including farms, landfills, & oil production. Reducing methane emissions can make a real difference in our fight against global warming. Simple actions, like improving waste management & supporting cleaner energy, can help limit its impact. By working together, we can address this issue & protect our environment for future generations. Every small effort counts, so let’s stay informed & take steps toward a cleaner, healthier planet!