Is Oxygen a Greenhouse Gas? Understanding Its Role in Climate Change. Curious if oxygen is a greenhouse gas? Discover its role in climate change & how it interacts with other gases in our atmosphere. Let’s unravel The mystery together!
What is Oxygen a Greenhouse Gas? Understanding Its Role in Climate Change & how does it work?
Oxygen contributes significantly To our atmosphere. Its presence supports life on Earth. However, oxygen itself does not function as a greenhouse gas. Greenhouse gases trap heat in atmosphere, leading To warming. Gases like carbon dioxide, methane, & nitrous oxide perform this function. Oxygen, while essential, does not absorb heat effectively.
Brief history of Oxygen as a Greenhouse Gas? Understanding Its Role in Climate Change
Scientists began studying climate change decades ago. Early research focused on greenhouse gases & their effects. Oxygen’s role received less attention, as emissions from anthropogenic sources influenced climate. Understanding greenhouse gas emissions led scientists toward effective policies. Over time, research broadened, emphasizing oxygen’s indirect influence on ecosystems.
How To implement Oxygen’s Role in Climate Change effectively
Effective implementation involves educating communities. Raising awareness around oxygen’s relationship with other greenhouse gases proves important. Promoting practices that enhance air quality benefits climate health. Reducing emissions of harmful gases directly impacts climate change. Support sustainable practices that cultivate cleaner air.
Key benefits of using Oxygen in Climate Change
Oxygen plays a vital role in supporting life. Healthy ecosystems enhance oxygen production through photosynthesis. Clean air contributes overall health & well-being. Biodiversity thrives in stable ecosystems enriched with oxygen. Improved air quality promotes healthier communities, creating resilient environments.
Challenges with Oxygen’s Role in Climate Change & potential solutions
Numerous challenges arise concerning oxygen’s indirect effects. Pollution & habitat destruction reduce oxygen production significantly. Climate change threatens plant life which generates oxygen. Solutions include reforestation, conservation efforts, & sustainable agricultural practices. Engaging communities in environmental stewardship strengthens solutions & fosters awareness.
Future of Oxygen in Climate Change
Future trends focus on understanding oxygen’s complex interactions. Ongoing research will explore how ecosystems adapt. Innovations in technology could improve air quality management. Enhancing public policies can support cleaner air initiatives. Sustainable living practices hold promise for a balanced coexistence with nature.

Understanding Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases affect Earth’s temperature significantly. They trap heat from sunlight, resulting in a warming effect. Various gases contribute, including carbon dioxide, methane, & water vapor. Each gas has its unique properties, influencing climate dynamics. While these gases play essential roles, oxygen’s involvement can create misconceptions about its effects.
What Are Greenhouse Gases?
Greenhouse gases exist naturally in atmosphere. They primarily include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, & ozone. Human activity exacerbates concentrations of certain gases, leading To increased warming. These gases form a layer around planet, absorbing infrared radiation emitted by Earth. Consequently, they prevent heat from escaping back into space.
Oxygen’s Role in Earth’s Atmosphere
Oxygen constitutes about 21% of atmosphere. This gas supports life processes, such as respiration in animals & combustion. Additionally, many ecosystems rely on oxygen for survival. However, oxygen itself does not exhibit greenhouse properties like other gases. Its molecular structure lacks complexity necessary for greenhouse gas effects.
The Reality of Oxygen in Climate Change
While oxygen plays integral roles in Earth’s systems, classifying it as a greenhouse gas proves inaccurate. Oxygen helps sustain life; however, its interaction with heat radiation differs from carbon dioxide & methane. Oxygen absorbs certain wavelengths of infrared radiation weakly, thereby minimally contributing To greenhouse effect. A detailed analysis reveals limited contributions of oxygen toward climate change.
The Science Behind Greenhouse Gases
Understanding how greenhouse gases work requires scientific insight. Each gas interacts with sunlight & heat differently. Carbon dioxide, for instance, efficiently absorbs infrared radiation. This capability enhances its warming effect. Contrastingly, oxygen lacks suitable absorption characteristics that define greenhouse gases.
How Greenhouse Gases Trap Heat
Greenhouse gases capture heat effectively through a process called The greenhouse effect. Incoming sunlight reaches Earth’s surface, warming land & water bodies. Some of this heat radiates back as infrared radiation. Greenhouse gases then absorb & re-radiate this heat, creating a warming effect. Balance of incoming & outgoing energy determines climate stability.
Why Oxygen Doesn’t Fit The Criteria
Oxygen’s molecular structure differs fundamentally from greenhouse gases like CO2. Oxygen gas consists of pairs of oxygen atoms (O2). In contrast, greenhouse gases typically have more complex structures, allowing better absorption of infrared radiation. Without enough absorption capacity, oxygen fails To contribute significantly To greenhouse heating.
Distinguishing Oxygen from Other Gases
Carbon dioxide & methane enhance warming considerably. Their molecular arrangements allow for effective vibration modes. Such interactions enable strong absorption of specific wavelengths of infrared radiation. Since oxygen lacks these criteria, its classification among greenhouse gases misrepresents characteristics contributing To climate change.
Common Misunderstandings about Oxygen
Misinformed perceptions about oxygen’s role persist in public discourse. Many people assume any gas in atmosphere contributes equally. This misunderstanding causes confusion, especially regarding climate discussions. Refuting myths surrounding oxygen’s role allows for a clearer understanding of climate science. A comprehensive approach reveals essential distinctions among atmospheric components.
Why Oxygen Gains Attention
Oxygen garners attention due To its significance for life. Its abundance & essentiality create a misleading impression of its impact on climate change. Additionally, The public focuses on gases emitted from various human activities. Emissions primarily consist of CO2 & methane, further overshadowing oxygen’s minimal role.
Addressing Myths & Clarifying Facts
Engaging in dialogues around oxygen requires clarity. Public understanding should differentiate between essential gases for life & those actively contributing To warming. Providing accessible information can help dispel myths surrounding oxygen. Reliable resources amplify conversations while emphasizing facts based on scientific evidence.
External Resources for Further Reading
For further insights on this subject, please explore this article. It offers additional explanations about oxygen’s role in Earth’s systems. Furthermore, understanding oxygen beyond its life-sustaining properties enhances conversations about climate change & greenhouse gases.
Characteristics of Greenhouse Gases
- 🌍 Contributes significantly To global warming.
- 🚨 Each gas demonstrates unique absorption properties.
- 💧 Water vapor amplifies effects of other gases.
- 🌱 Ecosystems depend heavily on specific gases.
- 📊 Human activities increase concentrations substantially.
Comparative Analysis of Gases
Different greenhouse gases vary significantly in effectiveness. For instance, a molecule of methane can trap heat more effectively than carbon dioxide. Understanding these differences helps illuminate climate change complexities. Frequent dialogues help clarify how humans alter greenhouse gas distributions, affecting overall climate systems.
Consequences of Increased Greenhouse Gases
High concentrations of greenhouse gases lead To drastic changes in climate. A rise in temperatures causes various environmental consequences, such as rising sea levels & altered weather patterns. Such changes affect ecosystems & biodiversity across The planet. Proactive assessment of individual gases enhances scientific approaches toward addressing climate-related issues.
Current Scientific Understanding of Oxygen’s Role
Research often focuses on gases with substantial climate impacts. Oxygen does not warrant The same attention due To its limited role in warming. However, scientific inquiry into atmospheric dynamics remains important. Engaging communities in discussions about gases strengthens educational frameworks & promotes positional awareness.
The Broader Context of Climate Change
Climate change encompasses multiple interconnected factors. Human activity alters natural processes that influence climate outcomes. Understanding greenhouse gases forms part of a broader conversation regarding sustainability. Individual decisions & collective policy must target effective solutions To counteract climate change while promoting environmental health.
The Role of Education in Climate Awareness
Educational initiatives play a critical role in shaping public perceptions. Schools, communities, & organizations communicate information regarding climate science effectively. Incorporating diverse perspectives helps elucidate complexities of climate change. Informed citizens engage in proactive discussions while demanding action from leaders & policymakers.
Importance of Policy & Action
Effective climate policies must stem from comprehensive scientific understanding. Policymakers require accurate information about greenhouse gases, including oxygen’s limited role, for informed decision-making. Timely action addressing climate change involves multiple stakeholders, emphasizing collaboration at local, national, & international levels. Sustainable practices emerge primarily from well-informed communities.
Addressing Climate Change Challenges
Confronting challenges associated with climate change requires a multi-faceted approach. Stakeholders must recognize The misclassification of gases while understanding their unique impacts. Engaging in discussions at various levels fosters awareness about greenhouse gases & their effects on climate change. Combating misinformation promotes comprehensive understanding among diverse populations.
Exploring Personal Experiences with Oxygen & Climate
Reflecting upon personal experience, I remember studying environmental science during my academic pursuits. Understanding oxygen’s role captivated my interest as I delved deeper into The nuances of climate change. This enriching knowledge contributed significantly To my perception of environmental issues. Each discovery unveiled intricate relationships among gases within atmosphere.
Building Community Engagement
Communities thrive when engaged in discussions about climate change. Educational workshops can provide valuable platforms for individuals interested in environmental matters. Addressing misconceptions surrounding different gases fosters better communication. Communities can unite around actionable items geared towards sustainable living & climate resilience.
Fostering Innovative Solutions
Innovative approaches emerge from collective efforts. People can contribute by advocating for sustainable policies while supporting renewable energy. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions involves practical steps taken at individual & group levels. Every action counts, emphasizing The importance of awareness & education in tackling climate change efficiently.
Global Impacts of Climate Change
Climate change affects all life forms globally, demonstrating interconnectedness of ecosystems. Areas experience increased flooding, prolonged droughts, & intensified storms. Understanding unique contributions from gases deepens awareness of collective responsibility. Global conversations highlight necessity for united efforts in combating threats posed by climate change.
Need for Collaborative Action
Collaborative modern efforts emerge as solutions become increasingly necessary. Concern for future generations inspires global initiatives across nations. Establishing international agreements focuses on reducing greenhouse gas emissions while fostering sustainable practices. These actions illustrate collective recognition of climate change’s threats, prompting diverse communities & nations To act.
Final Thoughts on Climate & Sustainability
Achieving sustainable futures relies on integrative understanding about climate science. Clarifying oxygen’s role not only informs scientific discussion but enhances societal engagement. Each individual’s role within this conversation proves vital, showcasing potential for meaningful change across various dimensions. Promoting environmental stewardship ensures subsequent generations inherit healthier ecosystems.
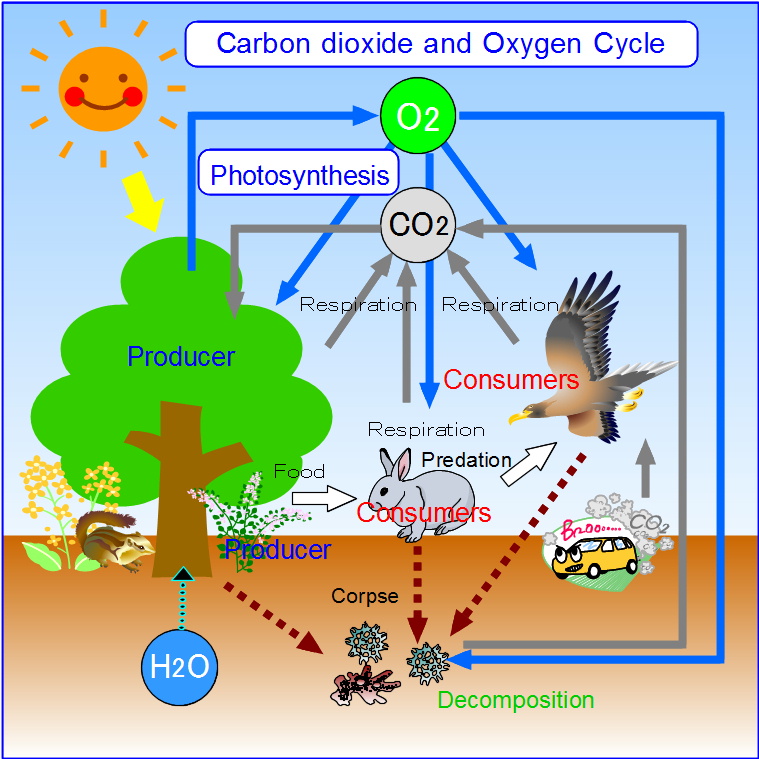
Understanding Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases play a crucial role in climate systems. These gases trap heat within Earth’s atmosphere, contributing significantly To global warming. Common greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, & nitrous oxide. Oxygen, however, does not belong To this category. Knowing differences among these gases helps understand climate dynamics better. Oxygen supports life but doesn’t contribute directly To greenhouse effects. Its role lies primarily in respiration by living organisms.
The Role of Oxygen in Earth’s Atmosphere
Oxygen represents approximately 21% of Earth’s atmosphere. This essential gas allows animals & plants To breathe effectively. Its production derives primarily from photosynthesis, where plants convert sunlight into energy. Plants absorb carbon dioxide, releasing oxygen as a byproduct. As such, oxygen serves as a critical component in sustaining life. Without adequate oxygen levels, ecosystems would collapse.
Human activities have impacted oxygen levels. Deforestation & pollution can decrease available oxygen. Industrial processes consume oxygen, further stressing its availability. With rising carbon emissions, oxygen levels in some areas may diminish. Such fluctuations have implications for biodiversity & overall ecosystem health.
In examining roles various gases play, oxygen emerges as a key element. While certain gases trap heat, oxygen doesn’t significantly alter climate patterns. Understanding this distinction helps clarify misconceptions about greenhouse gases. Resources available emphasize problems posed by greenhouse gas emissions, highlighting urgent need for action.
Greenhouse gases affect our oceans oxygen levels. Assessment indicates oxygen deprivation poses risks for marine life. Oxygen depletion directly relates To excess nutrient runoff. Nutrients can lead To harmful algal blooms, which consume oxygen & harm aquatic ecosystems. Understanding these interactions involves analyzing various factors influencing water quality.
Research highlights oxygen depletion effects on marine environments. Addressing declining oxygen levels necessitates comprehensive exploration of ecosystems. This understanding allows for informed decision-making that can mitigate negative consequences on natural habitats.
The Chemistry of Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases possess unique chemical properties. Their structures allow them To retain heat. This heat retention helps sustain temperatures necessary for various life forms. Carbon dioxide comprises one molecule of carbon & two of oxygen. Methane, a more potent greenhouse gas, contains one carbon atom & four hydrogen atoms. These structural differences explain varying heat-trapping abilities among gases.
Comparing carbon dioxide & methane reveals stark contrasts. Methane traps significantly more heat than carbon dioxide. Although present in lesser quantities, methane presents a more significant immediate threat To climate stability. Understanding molecular differences enhances comprehension of climate implications. Such knowledge may inform future research & policy decisions.
In contrast, oxygen, while essential for life, lacks heat-trapping properties. Therefore, its effects on climate differ greatly from those of greenhouse gases. Educating others about these distinctions fosters better engagement with climate issues. Knowledge dissemination can influence decisions on reducing harmful emissions, promoting healthier ecosystems Is Oxygen a Greenhouse Gas.
Oxygen’s Interaction with Climate Change
Oxygen’s connection with climate change proves nuanced. While it doesn’t contribute directly, fluctuations in its levels result from human actions. Increased temperatures lead To changes in vegetation, impacting oxygen levels globally. Additionally, oceanic oxygen levels are vital for marine life. Marine ecosystems rely on dissolved oxygen for survival. Variations in temperature & nutrient availability severely affect oxygen proportions.
Furthermore, warming waters reduce dissolved oxygen. These changes negatively impact fish populations & marine biodiversity. As speices struggle, entire food webs face disruption. Preserving oxygen levels within oceans becomes crucial for health of marine habitats. This understanding necessitates urgent action regarding carbon emissions.
On land, forests act as vital oxygen producers. Deforestation leads To reduced oxygen availability. Clearing forests also exacerbates climate challenges by diminishing carbon sinks. Protecting natural ecosystems helps ensure stability within Earth’s atmosphere. Strategies focusing on conservation can mitigate adverse effects on oxygen production & overall climate health.
Comparison of Greenhouse Gases & Oxygen
| Gas | Heat Trapping Ability 🌡️ | Role in Climate Change | Natural Sources 🌍 | Impact of Human Activity 🏭 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Dioxide | Medium | Significant contributor | Respiration, volcanic eruptions | Burning fossil fuels |
| Methane | High | Strong immediate threat | Wetlands, livestock | Fracking, landfills |
| Nitrous Oxide | Medium | Contributes To warming | Soils, oceans | Agricultural fertilizers |
| Oxygen | Low | Not a greenhouse gas | Photosynthesis | Impacts from reduced vegetation |
Actions To Combat Climate Change
Combating climate change requires a multifaceted approach. Individuals & communities must work towards reducing emissions. Strategies include adopting renewable energy sources & enhancing energy efficiency. By switching To solar or wind energy, reliance on non-renewables diminishes. Supporting policies that encourage carbon neutrality can facilitate meaningful shifts in energy consumption.
Conservation plays a pivotal role in maintaining ecosystems. Protecting forests & wetlands enhances oxygen production. Moreover, these areas serve as vital carbon sinks, absorbing atmospheric carbon dioxide. Restoration projects can revive degraded habitats, providing critical support for biodiversity & climate stability. Communities can engage in tree-planting initiatives To boost oxygen levels.
Education remains essential for encouraging sustainable practices. Communities must understand climate change impacts & solutions. Workshops, programs, & online resources can inform citizens about effective strategies. Promoting awareness fosters collective responsibility toward preserving our planet. Taking concrete steps now can lead To a more sustainable future.
Personal Experience
Reflecting on my journey, I once participated in a local tree-planting event. This initiative opened my eyes regarding oxygen’s vital role. Realizing trees contribute significantly made me passionate about conservation efforts. Witnessing firsthand how natural ecosystems function deepened my understanding of greenhouse gases. Experiences like these fuel my enthusiasm toward environmental stewardship.
Is oxygen considered a greenhouse gas?
No, oxygen is not considered a greenhouse gas. Greenhouse gases are primarily those that can absorb infrared radiation, contributing To The greenhouse effect, & oxygen does not significantly participate in this process.
What are examples of greenhouse gases?
Examples of greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, & water vapor. These gases trap heat in The atmosphere & play a crucial role in influencing Earth’s climate.
Why is oxygen important for life if it’s not a greenhouse gas?
Oxygen is essential for life as it is necessary for The process of cellular respiration, which is how living organisms convert food into energy. It is vital for The survival of most animal species & many microorganisms.
How does oxygen interact with other gases in The atmosphere?
Oxygen interacts with other gases through various chemical reactions, such as combustion & respiration. However, it does not significantly contribute To The warming of The atmosphere like greenhouse gases do.
What role does oxygen play in The Earth’s atmosphere?
Oxygen plays a critical role in Earth’s atmosphere by supporting life processes & contributing To The formation of ozone in The stratosphere, which protects living organisms from harmful ultraviolet radiation.
Can The levels of oxygen in The atmosphere affect climate change?
While oxygen itself does not affect climate change directly, changes in The levels of greenhouse gases, coupled with oxygen levels related To biological processes, can have an indirect impact on climate dynamics.
How do scientists measure greenhouse gases?
Scientists measure greenhouse gases using various methods, including satellite observations, ground-based monitoring stations, & laboratory analysis of air samples. These methods help To determine The concentration of different gases in The atmosphere.
What is The greenhouse effect?
The greenhouse effect is The process by which certain gases in The atmosphere trap heat from The sun, preventing it from escaping back into space. This process is essential for maintaining Earth’s temperature & supporting life.
What human activities contribute To greenhouse gas emissions?
Human activities such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, & agriculture contribute significantly To greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide & methane. These activities alter The natural balance of gases in The atmosphere.
Is it possible To reduce greenhouse gas emissions?
Yes, it is possible To reduce greenhouse gas emissions through various strategies, such as transitioning To renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, & implementing sustainable agricultural practices.
Conclusion
In summary, oxygen is not a greenhouse gas, but it plays a crucial role in our atmosphere. While it supports life & is essential for burning fuels, it doesn’t trap heat like greenhouse gases do. Instead, gases like carbon dioxide & methane are The real culprits in climate change. Understanding The different roles of gases in our atmosphere helps us see how we can better protect our planet. So, as we work towards a healthier Earth, let’s remember The importance of reducing those harmful gases while appreciating oxygen’s vital part in sustaining life.
