Is Nitrogen a Greenhouse Gas? Examining Its Role in Climate Change Impact. Curious if nitrogen is a greenhouse gas? Join us as we explore its role in climate change & how it affects our planet’s future. Let’s find out together!
What is Nitrogen a Greenhouse Gas? Examining Its Role in Climate Change Impact & how does it work?
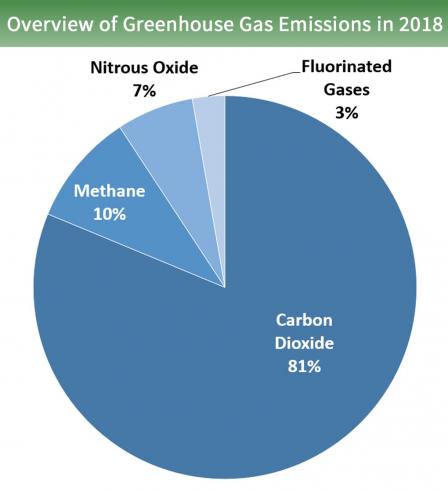
Nitrogen plays a crucial part in Earth’s atmosphere. However, nitrogen itself does not function as a greenhouse gas. Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, & nitrous oxide, which trap heat. Nitrogen’s role involves contributing indirectly through its compounds.
Brief history of Nitrogen a Greenhouse Gas? Examining Its Role in Climate Change Impact
Scientists discovered nitrogen in late 18th century. Analogous studies followed exploring other gases. Focus on greenhouse gases heightened during 20th century. Research demonstrated human activity influences these gases.
How To implement Nitrogen a Greenhouse Gas? Examining Its Role in Climate Change Impact effectively
Addressing nitrogen’s effects requires strategic measures. Regulatory frameworks should promote sustainable agriculture. Improved practices can reduce nitrous oxide emissions. Utilizing cover crops aids in nitrogen absorption. Precision farming enhances nutrient management greatly.
Key benefits of using Nitrogen a Greenhouse Gas? Examining Its Role in Climate Change Impact
Benefits include improving air quality across regions. Enhanced soil health leads directly To better crop yields. Efficient nitrogen management reduces pollution significantly. Agriculture practices adapt, ensuring sustainability for future generations.
Challenges with Nitrogen a Greenhouse Gas? Examining Its Role in Climate Change Impact & potential solutions
Challenges arise from excessive nitrogen usage. Overapplication leads To water contamination & soil degradation. Addressing these concerns requires integrated solutions. Governments & farmers must collaborate effectively for change. Educating stakeholders proves essential for reducing nitrogen footprint.
Future of Nitrogen a Greenhouse Gas? Examining Its Role in Climate Change Impact
Future trends showcase increasing awareness surrounding nitrogen management. Innovative technologies promise efficient nutrient use. Policies will likely evolve, encouraging best practices. Collaboration across sectors remains vital for sustainable progress. Emphasis on education & research will drive positive change.
Understanding Nitrogen’s Role
Nitrogen plays a vital role in our environment. While most know nitrogen as a harmless gas, its behavior can become complex under certain conditions. This complexity contributes significantly To climate change discussions. By exploring nitrogen’s relationship with greenhouse gases, a clearer understanding of its impact emerges. For those interested, read this article that explains four reasons why our world needs limits on nitrogen pollution here.
Components of Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases include a range of components. Carbon dioxide remains a primary player, along with methane & nitrous oxide. While nitrogen gas itself does not act as a greenhouse gas, its compounds can significantly affect climate change. Nitrous oxide, for instance, directly contributes as a potent greenhouse gas. Understanding different nitrogenous compounds provides insights into climate change challenges.
Human activities contribute largely towards increasing greenhouse gases. Agriculture, industry, & energy sectors all release various nitrogen compounds into The atmosphere. These actions manifest more frequent extreme weather events. Additionally, these gases exacerbate existing environmental issues. Learning about these interactions helps us devise better solutions.
Nitrogen’s various oxides are crucial in understanding greenhouse effects. Nitrogen oxides serve as significant pollutants harming air quality. Their impact on climate change warrants attention. Each contribution adds complexity To discussions about greenhouse gases & global warming. Awareness around these gases can create pathways for effective environmental policies.
Different Forms of Nitrogen Compounds
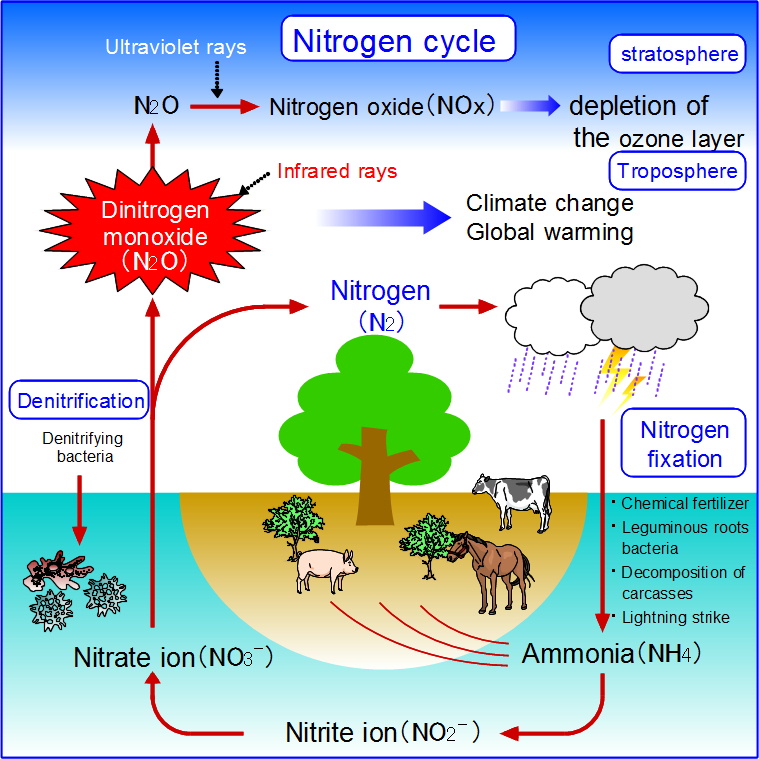
Nitrogen undergoes various transformations in nature. Atmospheric nitrogen exists predominantly as dinitrogen (N2). While it constitutes significant portions of air, dinitrogen remains inert & non-reactive. However, its transformation into other compounds leads To diverse consequences. For example, nitrogen oxides (NOx) result from combustion processes. Various industries release these gases into The atmosphere.
Ammonia also forms through agricultural practices. Livestock waste, fertilizers, & industrial processes contribute significantly here. Ammonia poses its own threats through atmospheric reactions. Its conversion into pollutants impacts air quality & health. Understanding these transformations offers insight into nitrogen’s broader environmental implications.
Nitrous oxide (N2O), another significant form of nitrogen, has serious climate implications. Its greenhouse potential compares unfavorably against carbon dioxide. While less abundant, a single molecule of nitrous oxide traps significantly more heat than carbon dioxide. Thus, managing this compound proves vital in grappling with climate change.
The Impact of Nitrogen Emissions
Nitrogen emissions from human activities affect ecosystems. Fertilizer runoff contributes significantly To this phenomenon. Consequently, water bodies experience nutrient loading. Algal blooms thrive in these enriched environments, resulting in dead zones. Such occurrences lead To biodiversity loss & ecosystem damage. Therefore, managing nitrogen emissions plays a crucial role in protecting ecological balance.
Traffic & industrial outputs contribute more pollutants. Vehicles emit nitrogen oxides, exacerbating air quality issues. Poor air quality correlates with respiratory diseases. Various health implications underscore our urgent need To address nitrogen pollution. Regular monitoring can help mitigate these adverse effects.
Moreover, climate change directly induces shifts in weather patterns. Increasing temperatures interact with nitrogen emissions, causing further complications. More storms & floods can dilute contaminants into water systems. Consequently, more regions experience negative health impacts, creating societal burdens. Therefore, management of nitrogen sources remains imperative.
Global Efforts & Policies
Global initiatives aim at reducing nitrogen emissions. Various countries adopt policies addressing air pollution. For example, The United Nations promotes several strategies. Nations collaborate towards reducing greenhouse gas outputs. Understanding these guidelines helps implement effective local policies. Adopting best practices can reduce nitrogen’s adverse environmental impact.
Compliance with international agreements supports these efforts. Agreements like The Paris Accord highlight concrete action plans. Nations commit To monitoring & reducing emissions consistent with climate objectives. Collaborative efforts depict promising trends in changing nitrogen management. Consequently, engagement at global, national, & local levels proves essential.
Numerous organizations advocate for improved nitrogen use. Partnerships between governments, NGOs, & communities promote awareness. Educational programs raise awareness about nitrogen’s potential harms. Fostering community involvement encourages sustainable practices. Empowering local actions promotes real change, supporting larger initiatives.
Connecting Nitrogen Management with Climate Change
Linking nitrogen management & climate change outcomes emphasizes importance. Properly managing nitrogen emissions reduces greenhouse gas effects. Farmers adopting precision agriculture techniques can optimize fertilizer use. This practice ultimately minimizes runoff & pollution. Moreover, it enhances crop sustainability, benefiting both environment & economy.
Innovations in technology support better nitrogen management. Developments in monitoring systems provide invaluable data. This technology enables policymakers To make informed decisions. Additionally, industries can adopt cleaner practices aligned with current sustainability goals. Transitioning towards greener solutions highlights opportunities for improved nitrogen management.
Public engagement further galvanizes these initiatives. Educated communities advocate for shouldering responsibility. Fostering awareness about nitrogen’s impact empowers grassroots movements. Local actions contribute towards broader environmental strategies. Together, these steps create a narrative for positive change towards sustainability.
Potential Solutions for Nitrogen Pollution
Addressing nitrogen pollution necessitates diverse solutions. Policy frameworks should establish standards for emissions. Stricter regulations foster compliance among industries. Additionally, encouraging research on alternative fertilizers opens up new pathways. Identifying & implementing sustainable agricultural practices remains critical.
Public transportation & clean energy initiatives are also crucial. Transitioning away from fossil fuels reduces nitrogen pollutants. Implementing public transit & active transportation improves air quality. Investments in renewable resources provide further avenues for reducing nitrogen contributions.
Community-led initiatives represent a promising avenue. Local citizen groups can drive awareness & action. Education campaigns can raise consciousness about nitrogen issues. Such grassroots efforts promote sustainable practices within communities. Enhancing community engagement builds stronger connections To The cause.
Impact on Biodiversity & Ecosystems
Nitrogen pollution profoundly impacts biodiversity. Ecosystems exposed To excess nitrogen experience significant alterations. Aquatic systems bear The brunt of nutrient loading. Algal blooms result from surface runoff, disrupting aquatic life. Consequently, these ecosystems face declining biodiversity levels. Monitoring key indicators can help assess these changes.
Moreover, terrestrial ecosystems also face nutrient imbalances. Habitats are transformed, potentially leading To species loss. Sensitive plant communities struggle in nitrogen-enriched environments. Over time, plant diversity decreases, altering interactions within ecosystems. Our understanding of these impacts helps inform conservation strategies.
The intricate balance of ecosystems requires ongoing study. Tracking nitrogen’s influence equips scientists with data. This information can inform better management practices. Moreover, policymakers can develop strategic initiatives based on findings. Collaborative research yields critical insights into nitrogen’s ecological effects.
Challenges in Nitrogen Management
Addressing nitrogen pollution presents multiple challenges. One primary issue stems from industry resistance. Industries often prioritize profits over environmental responsibilities. Overcoming this inertia requires innovative regulatory measures. Engage industry stakeholders in collaborative dialogues. This approach builds mutual understanding & promotes shared responsibility.
Additionally, insufficient public awareness remains a barrier. Many individuals lack knowledge about nitrogen’s environmental impacts. Program initiatives should aim at increasing public education. Developing clear messaging helps enhance understanding. Through education, communities can advocate for change effectively.
Resource limitations also play a role in addressing nitrogen challenges. Financial investments are crucial for research & implementation. Governments & organizations must allocate funding towards meaningful solutions. Supporting grassroots initiatives can lead To practical change. Ensuring funding channels align with sustainable approaches heightens impact.
Future Outlook on Nitrogen Management
Looking ahead reveals both challenges & opportunities. Ongoing advancements in technology present promising solutions. Innovations in agricultural practices enhance nutrient efficiency. Measurement systems improve tracking of nitrogen emissions. These developments could translate into better management strategies over time.
Collaboration across sectors will prove essential. Industry stakeholders, governments, & communities must engage harmoniously. Coordinating efforts leads towards shared goals & outcomes. Establishing clear objectives forms a foundation for future initiatives. Developing comprehensive plans sustains momentum for reducing nitrogen pollution.
Finally, constant monitoring remains crucial. Regular assessment of nitrogen levels guides policy adjustments. Ensuring transparency in emissions reporting builds trust. Collaborative frameworks create a unified approach towards achieving nitrogen management goals. Through sustained efforts, a healthier environment can emerge.
Features of Nitrogen Management Strategies
- Increased public awareness campaigns 📢
- Development of new technologies ⚙️
- Policy frameworks & regulations 📜
- Community-led initiatives 🤝
- Sustainable agricultural practices 🌾
Personal Experience with Nitrogen Management
During my time volunteering with a local environmental group, my perspective on nitrogen’s impact transformed. Observing direct consequences of excess nitrogen challenged my understanding. Participating in community initiatives highlighted practical ways To mitigate pollution.
Throughout discussions with experts, new insights became apparent. Learning about innovative agricultural techniques fueled a passion for advocacy. This experience illustrated The collective effort needed in addressing nitrogen issues.
Ultimately, passionate conversations around environmental sustainability drive meaningful change. Collaborating with dedicated individuals fosters a sense of camaraderie. These experiences underscore our collective responsibility towards a healthier environment.
Understanding Nitrogen: Composition & Characteristics
Nitrogen forms around 78% of Earth’s atmosphere. This element, known as a major atmospheric gas, possesses unique properties. Chemically, nitrogen exists in diatomic molecules, making it stable & inert under normal conditions. This inert nature keeps nitrogen from causing reactions easily. Thus, nitrogen remains abundant in various ecosystems.
Unlike greenhouse gases, nitrogen does not absorb infrared radiation effectively. This raises an important question: What role does nitrogen play in climate dynamics? Knowledge of nitrogen’s behavior helps scientists understand its ecological effects. Ongoing studies confirm that nitrogen’s abundance impacts various environmental processes.
Atmospheric nitrogen serves vital functions beyond being merely a component. Active roles include supporting biological processes, such as nitrogen fixation. Plants utilize fixed nitrogen compounds for growth, showcasing its importance. In this light, understanding nitrogen requires examining its interactions in different contexts.
Nitrogen Compounds & Their Impact on Climate Change
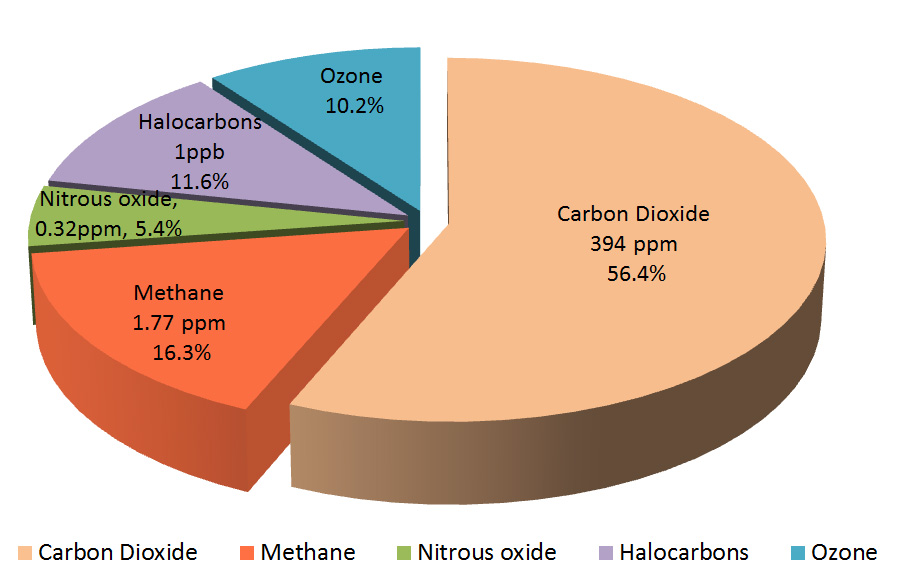
Nitrogen oxides (NOx) significantly affect climate change. These compounds, primarily created through combustion processes, contribute To atmospheric warming. NOx contributes directly To ozone formation in lower troposphere levels, reinforcing greenhouse gas effects. This relationship highlights The concerning aspect of nitrogen-based contaminants.
Moreover, nitrous oxide (N2O) emerges as a potent greenhouse gas. It possesses a much higher global warming potential than carbon dioxide. Nitrous oxide originates from agricultural practices, including fertilization & soil management. For more insights, consider this scientific article detailing nitrous oxide’s impact.
Furthermore, nitrous oxide plays a crucial role in stratospheric ozone depletion. This compound actively participates in atmospheric chemistry, leading To lasting consequences. Its presence illustrates nitrogen’s ability not just as an inert gas but as an active contributor To climate change dynamics. Ultimately, understanding nitrogen compounds adds depth To climate discussions.
Comparative Analysis of Greenhouse Gases
| Greenhouse Gas | Source | Global Warming Potential (GWP) | Atmospheric Longevity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrous Oxide (N2O) 🌍 | Agricultural activities | 298 times CO2 | 114 years |
| Carbon Dioxide (CO2) 🌱 | Fossil fuel burning | 1 | 300 years |
| Methane (CH4) 🍃 | Livestock, landfills | 25 times CO2 | 12 years |
Nitrogen Fertilization: Environmental Consequences
Nitrogen fertilization effects extend beyond agriculture, impacting ecosystems. Excess nitrogen runoff leads To water bodies experiencing eutrophication. This process triggers algal blooms, depleting oxygen levels necessary for aquatic life. Consequently, biodiversity suffers, causing ecosystem imbalance.
One common consequence involves hypoxic zones. These areas, with depleted oxygen, become uninhabitable for marine organisms. Nitrogen pollution significantly alters nutrient cycling within ecosystems. Understanding these dynamics showcases The interconnectedness between human activities & environmental changes.
Innovative practices can mitigate these negative impacts. Employing sustainable agriculture techniques, such as precision farming, offers a solution. Balancing nitrogen application minimizes runoff, reducing harmful consequences. This approach highlights a proactive stance towards maintaining ecological integrity.
Nitrogen in Climate Models
Understanding nitrogen’s role involves integrating it into climate models. These models help predict future climate scenarios, considering nitrogen dynamics. Accurate representation of nitrogen effects provides clearer insights into climate predictions.
Atmospheric chemistry models account for nitrogen compounds, including NOx & N2O. These models simulate interactions that influence ozone formation & global temperatures. Incorporating nitrogen accurately improves predictions of climate changes over time Is Nitrogen a Greenhouse Gas.
Research interlinks nitrogen cycles with carbon & water cycles. Such connections enhance our understanding of interaction between various elements. Detailed modeling informs policymakers about potential climate actions needed for mitigation.
Community Initiatives & Nitrogen Management
Communities can play a role in addressing nitrogen issues. Local initiatives promote awareness about nitrogen’s impact on environment. Engaging citizens allows for collaborative solutions. Workshops, seminars, & educational campaigns highlight sustainable nitrogen practices.
Adopting community-driven approaches minimizes nitrogen pollution. Practices include promoting native planting & composting. These initiatives create a more resilient ecosystem, fostering community engagement. Collective actions contribute positively towards reducing nitrogen footprints.
Collaboration among local agencies aids in effective nitrogen management. Information sharing facilitates innovative solutions tailored for specific regions. Such efforts encourage communities worldwide To take responsible actions against nitrogen pollution.
Personal Experience with Nitrogen Management
During a recent environmental project, I engaged with local farmers. Understanding nitrogen’s impact revealed how pivotal sustainable practices are. Farmers adopted methods, emphasizing precision & responsibility. Witnessing their commitment inspired hope in addressing nitrogen pollution challenges.
Conclusion: Implications for Future Research
Future climate research must emphasize nitrogen’s role. Comprehensive studies exploring nitrogen compounds promise richer insights. Such research ultimately supports effective policies & sustainable practices in combating climate change. Continuous engagement with nitrogen dynamics shapes ecological discourse moving forward.
Is nitrogen considered a greenhouse gas?
Nitrogen itself is not considered a greenhouse gas. Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, & nitrous oxide, but nitrogen is primarily inert in The atmosphere & does not contribute To The greenhouse effect.
How does nitrogen affect climate change?
While nitrogen is not a greenhouse gas, it can influence climate change indirectly. For example, reactive nitrogen compounds can lead To The formation of other greenhouse gases, such as nitrous oxide, which is a potent greenhouse gas.
What role does nitrogen play in agriculture?
Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for plant growth, & its application in fertilizers can enhance crop yields. However, excessive use of nitrogen fertilizers can lead To increased emissions of nitrous oxide, contributing To climate change.
Does nitrogen contribute To air quality issues?
Yes, while nitrogen itself is not a pollutant, nitrogen oxides (NOx), which are gases formed from nitrogen & oxygen during combustion processes, can contribute To air pollution & The formation of ground-level ozone, which affects air quality.
What is The difference between nitrogen & nitrous oxide?
Nitrogen (N2) is a stable, inert gas that makes up about 78% of The atmosphere. In contrast, nitrous oxide (N2O) is a greenhouse gas that has significant warming potential & is produced from agricultural & industrial activities.
Can increasing nitrogen levels in The atmosphere have environmental impacts?
Yes, increasing levels of reactive nitrogen in The atmosphere can lead To various environmental impacts, including eutrophication of water bodies, ecosystem imbalances, & increased greenhouse gas emissions.
What human activities contribute To reactive nitrogen emissions?
Human activities such as The use of nitrogen-based fertilizers, fossil fuel combustion, & industrial processes are major contributors To reactive nitrogen emissions, which can indirectly affect climate & air quality.
How does nitrogen cycle influence greenhouse gas emissions?
The nitrogen cycle, which involves The transformation of nitrogen through various chemical forms, plays a crucial role in The production of nitrous oxide. Disruptions in this cycle, often due To human activities, can increase greenhouse gas emissions.
Are there any benefits To increasing nitrogen levels in The atmosphere?
While excessive nitrogen can have negative environmental impacts, controlled increases in nitrogen levels, especially in agricultural practices, can enhance plant growth & crop productivity, contributing To food security.
What can be done To reduce nitrogen-related environmental issues?
Strategies such as optimizing fertilizer use, adopting sustainable agricultural practices, improving waste management, & reducing fossil fuel consumption can help mitigate The environmental impacts of excessive nitrogen emissions.
Conclusion
In summary, nitrogen itself isn’t a greenhouse gas like carbon dioxide or methane. However, it plays an important role in our environment. It can contribute To The formation of other greenhouse gases through processes like agriculture & industrial activities. So, while nitrogen isn’t directly responsible for warming The planet, it’s involved in The bigger picture of climate change. To tackle climate issues effectively, we need To think about how nitrogen is used & managed. By making smarter choices, we can help reduce its indirect impacts on our climate. Every little effort counts in protecting our Earth!