How Greenhouse Gases Contribute to Global Warming and Their Impact on Our Planet. Discover how greenhouse gases trap heat & lead To global warming. Learn about their effects on our planet & why it’s important To reduce them for a healthier future.
What is How Greenhouse Gases Contribute To Global Warming & Their Impact on Our Planet & how does it work?
Greenhouse gases trap heat from sun. This warming effect creates a greenhouse effect. Common gases include carbon dioxide, methane, & nitrous oxide. Human activities release vast amounts of these gases. Industrial processes, transportation, & deforestation contribute significantly. These gases encircle Earth, retaining warmth & altering climate. Rising global temperatures lead To severe environmental changes.
Brief history of How Greenhouse Gases Contribute To Global Warming & Their Impact on Our Planet
Awareness of greenhouse gas effects began in 19th century. Scientists first studied carbon dioxide’s impact on climate. Research continued into 20th century, revealing alarming trends. Global temperatures began rising alongside industrialization. In 1970s, recognition of pollution’s danger grew. United Nations established climate summits starting in 1992. Efforts continue worldwide, pushing for reduced emissions & policies.
How To implement How Greenhouse Gases Contribute To Global Warming & Their Impact on Our Planet effectively
Implementing effective changes requires collective action. First, transition toward renewable energy sources. Solar, wind, & hydroelectric power help reduce emissions. Next, encourage sustainable transportation habits. Public transit, biking, & electric vehicles support emissions reduction. Additionally, promoting energy efficiency in homes & businesses proves beneficial. Lastly, governments must enforce regulations & incentives.
Key benefits of using How Greenhouse Gases Contribute To Global Warming & Their Impact on Our Planet
Adopting sustainable practices offers numerous benefits. Reducing greenhouse gases enhances air quality. Improved air quality leads To better public health. Transitioning To renewables creates jobs in green sectors. Utilizing energy-efficient technologies decreases costs long-term. Protecting ecosystems preserves biodiversity & natural resources. Sustainable practices contribute toward a stable climate.
Challenges with How Greenhouse Gases Contribute To Global Warming & Their Impact on Our Planet & potential solutions
Multiple challenges exist in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Economic interests often conflict with environmental goals. Industries resistant toward change prioritize profits over sustainability. Political disagreements hinder comprehensive climate policies. Education about climate change remains insufficient. Solutions involve enhancing public awareness & engagement. Collaboration among nations further aids progress in this area.
Future of How Greenhouse Gases Contribute To Global Warming & Their Impact on Our Planet
Future developments aim for significant emissions reductions. Technological advancements promise cleaner energy solutions. Innovations in carbon capture & sequestration technologies emerge. Public awareness campaigns foster individual responsibility & action. Global cooperation may enhance treaty effectiveness among nations. Sustainable practices likely become fundamental in development plans. Urgent action now matters more than ever.
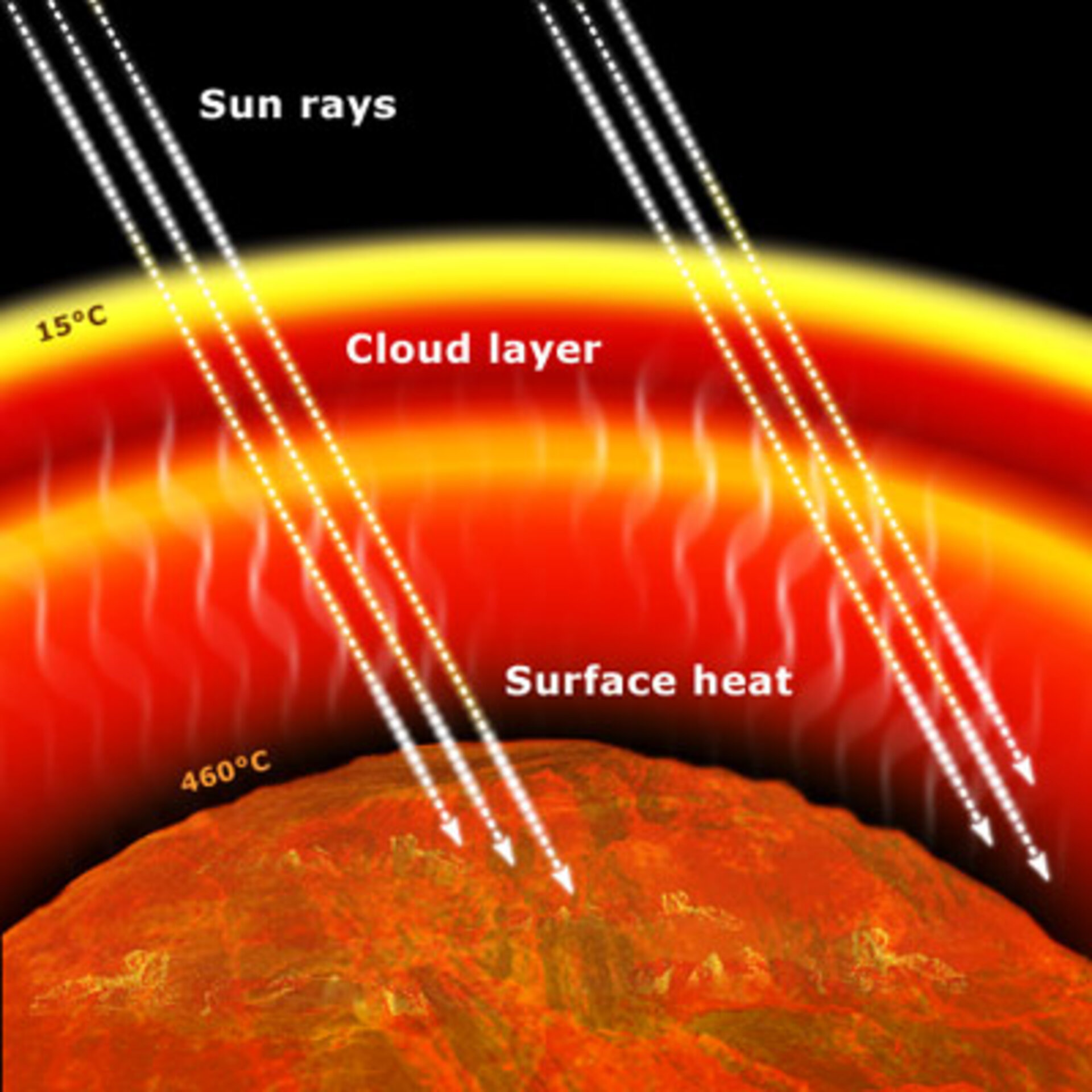
Understanding Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases play a crucial role in Earth’s atmosphere. Their concentrations determine how much solar heat remains on our planet. Common greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), & fluorinated gases. Each gas has a unique chemical structure, contributing differently To global warming. CO2, for example, has a long atmospheric lifetime & emits energy very effectively. This characteristic makes CO2 a significant greenhouse gas for climate change.
Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels & deforestation, have increased greenhouse gas levels. These actions have serious consequences for Earth’s climate system. Increasing concentrations can create a feedback loop, further amplifying warming. For more information about climate change science, visit EPA’s Climate Change Basics.
Natural processes also release these gases, such as volcanic eruptions & respiration. However, anthropogenic emissions greatly overshadow natural sources. For understanding their impact, it’s essential To analyze emission sources, types, & overall contributions To climate change. In many regions, human-induced activities have accelerated gas accumulation, disrupting Earth’s climate equilibrium. This drastic change can create irreversible consequences.
Carbon Dioxide & Its Effects
Carbon dioxide represents one of The most recognized greenhouse gases. Formed from combustion of fossil fuels & biomass, CO2 significantly contributes To climate change. Its long atmospheric lifespan allows it To persist for centuries, continuously trapping heat. Enhanced greenhouse effect causes Earth’s temperature To rise steadily over time. This increase leads To multiple environmental challenges.
Since The industrial revolution, carbon dioxide levels have skyrocketed. These emissions primarily stem from energy production, transportation, & industrial processes. Monitoring CO2 levels provides a crucial understanding of global warming trends. For instance, NASA’s Earth Observing System monitors these changes. To explore more, check Global Temperatures.
Impacts of increased CO2 levels extend beyond heat retention. Ocean acidification occurs when CO2 dissolves in ocean waters, affecting marine life. Coral reefs, in particular, suffer immense damage from rising temperatures & acidification. Therefore, addressing CO2 emissions provides a pathway toward a more sustainable future.
Methane Emissions & Their Significance
Methane represents a more potent greenhouse gas than carbon dioxide. Although present in smaller quantities, its heat-trapping ability dwarfs CO2 over short periods. Major sources of methane include agricultural practices, landfills, & natural gas production. Livestock farming contributes significantly as well, producing methane during digestion.
Due To its potency, even small increases in methane levels can influence atmospheric warming. Keeping track of methane emissions remains essential for climate change mitigation strategies. Reducing methane outputs proves vital for quick impacts on global temperatures.
In addition, methane significantly influences air quality. It reacts with other pollutants, creating ground-level ozone, a harmful air pollutant. Addressing methane emissions thus improves both climate & public health. Strategies can involve improved agricultural practices & better waste management.
Nitrous Oxide & Agricultural Practices
Nitrous oxide represents another critical greenhouse gas. Its molecular structure allows it To trap heat effectively, leading To global warming. Agricultural activities significantly contribute To nitrous oxide emissions. Common sources include synthetic fertilizers & manure management. These fertilizers release nitrous oxide into The atmosphere as microbes break down nitrogen compounds.
Reducing nitrous oxide emissions requires innovative agricultural techniques. Practices such as no-till farming & crop rotation can enhance soil health. Additionally, carefully managed fertilizer application reduces excess nitrogen runoff. These strategies promote carbon sequestration while tackling climate change.
Nitrous oxide also poses environmental risks outside agriculture. It contributes To ozone layer depletion, affecting climate patterns globally. Mitigating nitrous oxide emissions requires a multifaceted approach across various sectors. From agriculture To industry, each sector must recognize its responsibility.
Fluorinated Gases & Their Impact
Fluorinated gases encompass a group of synthetic gases utilized in various applications. These gases include hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), & sulfur hexafluoride (SF6). Though present in smaller quantities, their global warming potential remains significantly higher than carbon dioxide. For this reason, even minimal emissions can disproportionately affect overall warming.
The industrial sector commonly uses fluorinated gases, highlighting their continuing relevance. Although regulations exist, challenges remain in reducing their use. Alternatives must be developed, whereas stringent policies can facilitate lower emissions. This approach encourages innovation & investment in green technologies.
Moreover, fluorinated gases persist in The atmosphere for extended periods. Therefore, reducing their emissions presents a long-term climate solution. As industries transition away from these gases, a noteworthy impact on global warming will become apparent. Sustainable practices must become standard in research & development.
Feedback Mechanisms in Climate Change
Feedback mechanisms amplify The consequences of greenhouse gas emissions. Positive feedback loops, for instance, occur when warming leads To further emissions. For example, melting ice reduces Earth’s albedo. Darker surfaces absorb more sunlight, further accelerating warming. This scenario creates a vicious cycle, complicating climate stabilization efforts.
Additionally, permafrost thaw releases stored greenhouse gases. As these gases escape, global temperatures rise, causing even more thawing. Thus, understanding feedback mechanisms remains vital for prediction models & climate strategies. The complexity of these interactions necessitates a multitiered approach.
Scientists continuously study feedback mechanisms. Their findings aid in enhancing climate models, improving prediction accuracy. This research helps policymakers develop effective strategies for emission reductions. Integrating scientific knowledge into decision-making can prompt immediate effects on global warming trends.
Climate Change & Biodiversity Loss
Climate change severely threatens biodiversity across ecosystems. Species struggle To adapt rapidly To changing temperatures & habitats. Altered weather patterns disrupt migration routes & breeding seasons. Consequently, many species face extinction, leading To a collapse of ecosystems.
For instance, coral reefs experience bleaching events triggered by high temperatures. Loss of biodiversity affects food systems & ecological balance. Maintaining healthy ecosystems proves essential for climate resilience. Therefore, preserving biodiversity must remain a priority in climate action plans.
Strategies for conserving biodiversity include creating protected areas & restoring habitats. Engaging communities in conservation initiatives fosters collective responsibility. Promoting sustainable practices also encourages coexistence between humans & wildlife. Ultimately, a holistic approach addresses climate change while nurtures biodiversity.
Mitigation Strategies for Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Addressing greenhouse gas emissions requires concerted global efforts. Various strategies exist for reducing emissions across sectors. Transitioning To renewable energy sources forms a foundational element of mitigation. Solar, wind, & geothermal technologies produce clean energy with lower emissions.
Additionally, improving energy efficiency enhances existing infrastructure. Investing in energy-smart technologies reduces energy consumption while minimizing costs. Implementing stricter emission regulations promotes innovations in various industries as well.
Individuals can also make a difference. Simple changes in daily habits impact emissions positively. Reducing meat consumption, utilizing public transportation, & conserving energy can drive significant reductions. Collective efforts make a measurable difference in mitigating climate change.
- 🌍 Increased awareness of greenhouse gases
- 🌱 Implementation of sustainable agricultural practices
- 🌊 Restoration of natural ecosystems
- 🏙️ Transition toward renewable energy
- 🔄 Enhancing recycling & waste management
- 🚶♂️ Promoting public transportation usage
- 💡 Advancing energy-efficient technologies
International Agreements & Climate Action
Global efforts through international agreements strive for comprehensive climate action. Treaties such as The Paris Agreement aim To limit greenhouse gas emissions. Countries commit through nationally determined contributions (NDCs) towards significant reductions. Tracking progress remains essential for holding nations accountable.
Furthermore, international cooperation fosters sharing of resources & technology. Developed nations must aid developing countries in transitioning toward sustainable practices. Assisting these nations accelerates global progress while addressing inequalities.
Investing in adaptation strategies equates with comprehensively tackling climate change. Mitigation efforts alone remain insufficient for handling inevitable impacts. Resilience-building initiatives help communities withstand climate consequences while ensuring sustainability.
Final Thoughts on Greenhouse Gases & Our Planet
Understanding greenhouse gases & their impacts reveals critical insights into climate change. With heightened awareness, collective actions can mitigate adverse effects. As individuals, communities, & nations unite, hope for a more sustainable future remains. Achieving meaningful change requires persistent dedication & innovative strategies.
My experience at sustainability events showcased human potential. Individuals came together, exchanging ideas & solutions. It reaffirmed a shared commitment toward a healthier planet. Every effort counts in combating climate change.

Understanding Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases trap heat within atmosphere. This process crucially contributes toward global warming. Various gases play different roles. Carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, & fluorinated gases constitute main types. Each gas interacts uniquely with solar radiation. Understanding these interactions remains essential in addressing climate change issues.
Carbon dioxide comes from natural sources & human activities. Natural sources include volcanic eruptions & respiration by living organisms. Human activities largely derive from fossil fuel combustion & deforestation. Methane exists in much smaller quantities but holds significantly greater potency. It’s released during oil extraction, gas production, & livestock digestion.
Furthermore, nitrous oxide results from agricultural practices, land-use changes, & various industrial processes. Fluorinated gases, though less common, contribute substantially due To their long atmospheric lifetimes. Each gas possesses distinct global warming potential. This variability amplifies concerns regarding emissions management & reduction.
How Greenhouse Gases Affect Global Warming
Global warming stems from excessive greenhouse gas emissions. Increased concentrations lead To higher atmospheric temperatures. Consequently, Earth’s average temperature rises over time. Unchecked warming trends carry devastating consequences for ecosystems & human societies. Notably, this trend disrupts weather patterns, leading To extreme weather events.
Extreme events, such as hurricanes & droughts, affect agriculture & water supplies. Such shifts threaten food security & human health. Rising temperatures also lead To glacier melt, raising sea levels. Flooding poses significant risks for coastal communities & habitats. This accelerates displacement & loss of biodiversity.
For a comprehensive understanding of greenhouse gas emissions, visit EPA’s greenhouse gas sources. Additionally, consult resources on climate change causes through United Nations site. Both platforms offer vital insights & valuable information concerning emissions & their impacts.
Major Greenhouse Gases in Detail
Carbon dioxide constitutes most prevalent greenhouse gas. It accumulates through human activities more rapidly compared with natural processes. This accumulation leads directly To enhanced greenhouse effect. Elevated levels heat atmosphere, shifting climatic conditions considerably.
Methane, on another hand, possesses much higher warming potential. Despite existing in smaller amounts, it traps more heat per molecule than carbon dioxide. Methane emissions stem mostly from agriculture, especially from cattle & rice paddies. Reducing methane emissions can yield significant climate benefits.
Nitrous oxide contributes further through agricultural activities. Its release during fertilizer application significantly increases greenhouse gas concentrations. Reducing use can mitigate its environmental impact. A concerted effort streams from reduced fertilizer application & improved agricultural practices.
Impact on Ecosystems
Climate change causes severe disruptions across ecosystems. Altered temperature & precipitation patterns challenge flora & fauna. Some species struggle To adapt or migrate, pushing biodiversity toward critical thresholds. Reefs, forests, & wetlands face unprecedented stress due To changing environmental conditions.
Coral reefs, highly sensitive ecosystems, suffer from rising temperatures. Coral bleaching occurs when stressed by heat, leading To widespread mortality. This impacts marine life, fisheries, & coastal communities dependent upon healthy reefs. Global warming threatens not only marine ecosystems but also food security.
Forests, once resilient, face increased vulnerability. Pests & diseases grow prevalent due To changes in climate. Deforestation further exacerbates carbon dioxide emissions. Sustainable forest management brings forth potential solutions, enhancing resilience while sequestering carbon.
Human Health Concerns
Global warming fosters numerous health challenges for populations worldwide. Increased temperatures enhance air pollution levels, triggering respiratory issues. Vulnerable communities face elevated risks, especially among children & The elderly. Heat-related illnesses correlated with climate change rising significantly.
Vector-borne diseases expand their ranges due To shifting climates. Regions once unsuitable for certain diseases now harbor outbreaks. Malaria & dengue fever migrate toward newly suitable areas, increasing populations vulnerable To these threats. Continuous monitoring remains necessary To adequately address evolving health risks How Greenhouse Gases Contribute to Global Warming.
Public health systems must adapt accordingly. Implementing strategies that mitigate health impacts holds paramount importance. This includes promoting awareness, investing in healthcare infrastructure, & prioritizing vulnerable communities. Individual & collective efforts significantly contribute toward better health outcomes.
Potential Solutions To Combat Emissions
Combating climate change demands multi-faceted approaches. Transitioning toward renewable energy sources represents crucial strategies. Solar, wind, & hydroelectric power provide sustainable alternatives, reducing greenhouse gas emissions significantly. Energy efficiency improvements can produce immediate results as well.
Furthermore, adopting sustainable agricultural practices presents another effective avenue. Techniques such as crop rotation, agroforestry, & organic farming enhance soil health. These methods boost carbon sequestration while reducing reliance on chemical fertilizers. A holistic view of agricultural impact provides needed change.
Lastly, investing in technology plays a vital role. Innovations in carbon capture & storage present promising prospects. Developing electric vehicles & promoting sustainable transportation further support emissions reduction targets. Collective global action ultimately drives effectiveness toward creating cleaner environments.
Comparative Analysis of Greenhouse Gases & Their Impact 🌍
| Greenhouse Gas | Global Warming Potential | Primary Source | Atmospheric Lifespan | Impact on Climate 🌡️ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Dioxide (CO2) | 1 | Fossil Fuel Combustion | Hundreds of years | Long-term warming |
| Methane (CH4) | 25 | Agriculture, Landfills | 12 years | Rapid warming |
| Nitrous Oxide (N2O) | 298 | Agricultural Fertilizers | 114 years | Significant warming |
| Fluorinated Gases | Varies (100-12,000) | Industrial Processes | Up To thousands of years | Prolonged warming |
Personal Experience with Greenhouse Gases
During a recent camping trip, I noticed changes in weather patterns. Unexpected storms disrupted our plans, showcasing climate variability. This experience reinforced my understanding of climate change impacts firsthand. Observing nature’s responses highlighted urgency for addressing greenhouse gas emissions.
Global Efforts on Climate Change
Countries worldwide commit toward international agreements. Initiatives, such as Paris Agreement, aim for substantial emission reductions. Collaborative efforts encourage countries To set ambitious targets. These agreements foster accountability & ensure progress through collective action.
Non-governmental organizations also play pivotal roles. Their advocacy & outreach raise public awareness. Education enhances understanding of climate science while promoting sustainable practices. Engaging communities fosters resilience amid changing environmental conditions.
Individuals contribute significantly through lifestyle choices. Reducing energy consumption, utilizing public transport, & adopting plant-based diets extend positive impacts. Collective grassroots efforts unite toward a common goal: Combatting climate change & securing a sustainable future.
What are greenhouse gases?
Greenhouse gases are atmospheric gases that trap heat from The sun & contribute To The greenhouse effect, which leads To an increase in Earth’s temperature.
How do greenhouse gases make The planet hotter?
Greenhouse gases absorb infrared radiation emitted from The Earth’s surface & re-radiate some of this energy back toward The surface, enhancing The warming effect.
What are some common greenhouse gases?
Common greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), & fluorinated gases.
What activities contribute To greenhouse gas emissions?
Activities such as burning fossil fuels for energy, deforestation, industrial processes, & agricultural practices contribute significantly To greenhouse gas emissions.
What role does carbon dioxide play in climate change?
Carbon dioxide is The most significant greenhouse gas released by human activities, & its increased concentration in The atmosphere results in enhanced greenhouse effect & global warming.
How does methane compare To carbon dioxide in terms of warming potential?
Methane has a much greater short-term warming potential than carbon dioxide, being over 25 times more effective at trapping heat in The atmosphere over a 100-year period.
What is The greenhouse effect?
The greenhouse effect is a natural process where certain gases in The Earth’s atmosphere trap heat, maintaining The planet’s temperature & making it livable.
What impact do greenhouse gases have on weather patterns?
Increased greenhouse gas concentrations can disrupt weather patterns, leading To more frequent & severe weather events such as storms, droughts, & heatwaves.
What can individuals do To reduce greenhouse gas emissions?
Individuals can reduce emissions by conserving energy, using public transport, reducing meat consumption, recycling, & supporting renewable energy initiatives.
Are there regulations in place To control greenhouse gas emissions?
Many countries have implemented regulations & international agreements, such as The Paris Agreement, aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions & combating climate change.
How do forests help mitigate greenhouse gas emissions?
Forests absorb carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, acting as carbon sinks that help reduce The amount of CO2 in The atmosphere.
What is The significance of The melting polar ice caps?
The melting of polar ice caps contributes To rising sea levels & changes in ocean circulation, which can further impact global weather & climate patterns.
Conclusion
In wrapping up, it’s clear that greenhouse gases play a big role in global warming. They trap heat in our atmosphere, leading To rising temperatures & impacting our planet in many ways, like stronger storms, melting ice, & changing weather patterns. These changes affect our daily lives, from The food we eat To The air we breathe. Understanding how these gases work helps us see why we must take action. By reducing our emissions & embracing cleaner energy, we can start To heal our planet & create a better future for ourselves & generations To come.
